FIGURE 2.
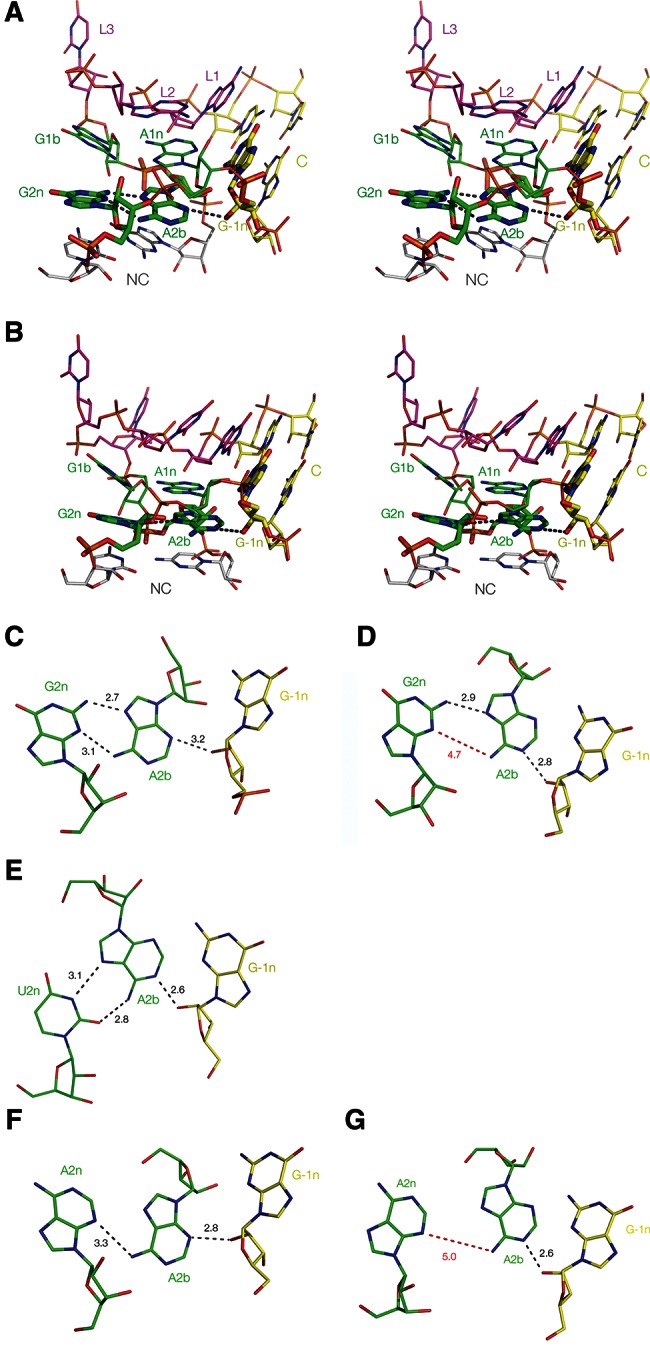
Two structural classes of k-turn. (A,B) Parallel-eye stereo images of two representative k-turns viewed from the side of the nonbulged strand, with G2n, A2b, and A−1n highlighted using a wider bond radius. The U4 snRNA k-turn (Vidovic et al. 2000) (A) is a member of the N3 class of k-turns, while H. marismortui Kt-38 (Ban et al. 2000) (B) is a member of the N1 class. (C–G) Relative disposition and interactions of nucleotides 2n, 2b, and −1n taken from the k-turns indicated below. Hydrogen bonds are indicated by broken lines and the distances (in Å) indicated. Distances too long to be considered hydrogen bonded are indicated in red. (C,D) U4 and Kt-38 k-turn structures, respectively. (E) Kt-23 of T. thermophilus. This has a uridine at the 2n position. (F,G) Two k-turns in which adenine replaces the normal guanine at the 2n position. F is taken from the structure of the SAM-I riboswitch k-turn with a G2nA substitution (Schroeder et al. 2011). G is taken from the structure of the SAM-I riboswitch where the normal k-turn has been replaced by Kt-23 of T. solenopsae (Schroeder et al. 2012).
