FIGURE 1.
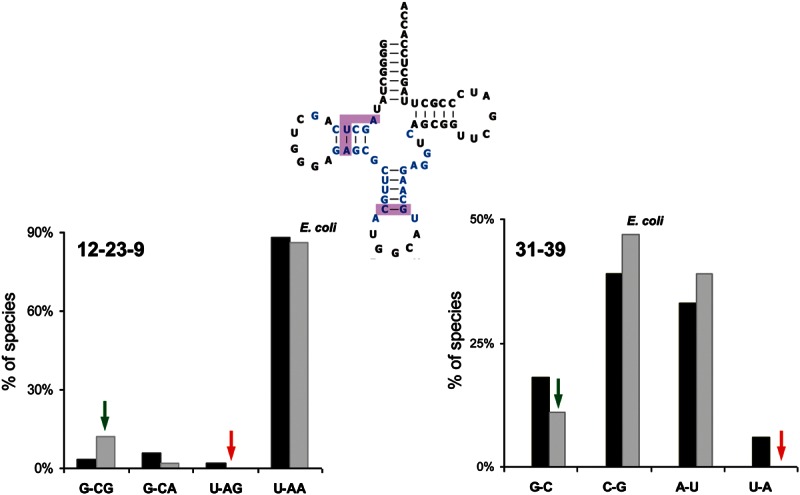
Using sequence conservation to direct the mutagenesis of nine base pairs and three base triples in the anticodon hairpin and tertiary core of E. coli tRNAAlaGGC (blue). The bar graphs compare the frequency of different 12-23-9 base triple sequences (left) and 31-39 base pair sequences (right) present among 97 bacterial tRNAAlaGGC (gray bars) with the corresponding sequences present among 3623 bacterial tRNAs of the D4V5 structural class (black bars). Nonconsensus mutations of E. coli tRNAAlaGGC (red arrows) are not present in any bacteria tRNAAlaGGC but are used in other tRNAs. Consensus mutations (green arrows) are present in tRNAAlaGGC from other species. Sequence conservation data and mutations chosen for all the base pairs and triples are in Table 1.
