FIGURE 9.
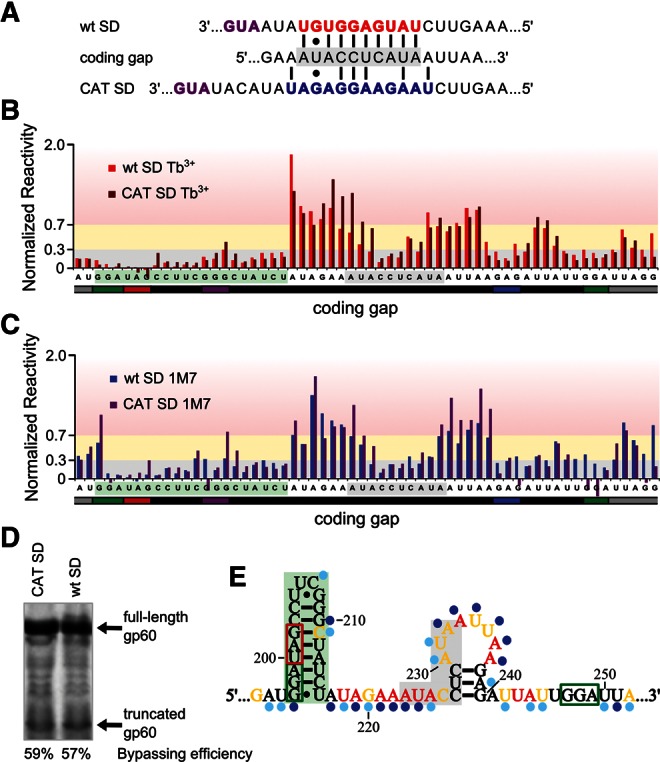
The coding gap reactivity does not change significantly in the absence of the wild-type gene 60 SD (wt SD). (A) Mutation of the wild-type gene 60 SD (red) to that of the chloramphenicol acetyl transferase (CAT) gene (blue). Start codons are purple, and the portion of the coding gap complementary to the wt SD is shaded in gray. (B) Comparison of reactivity of wt SD gene 60 (red) and CAT SD gene 60 (brown) coding gap nucleotides with Tb3+. The 5′ hairpin nucleotides are shaded in green, and the portion of the coding gap complementary to the wt SD is shaded in gray. (C) Comparison of reactivity of wt SD gene 60 (blue) and CAT SD gene 60 (purple) coding gap nucleotides with 1M7. (D) In vitro translation products of gene 60 with the wt or CAT SD. Bypassing efficiency for each template is indicated. (E) Secondary structure model of the coding gap region generated from probing data for CAT SD gene 60 mRNA (both Tb3+ and 1M7 probing generated models contain this coding gap structure). Shading is as described in B, and colors and symbols are as described in Figure 4.
