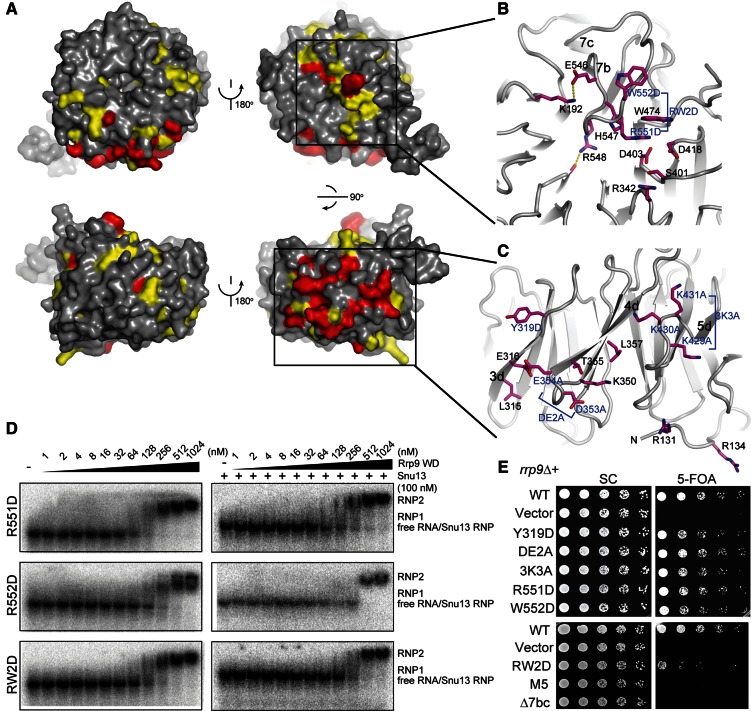
FIGURE 4.
Functional sites in the Rrp9 WD domain. (A) The conserved surface of the Rrp9 WD domain shown in four orientations. The residues with 97% and 80% conservation as defined in Figure 1 are colored red and yellow, respectively. (B,C) Close-up views of the top surface (B) and the side surface that spans blades 3 to 5 (C). The residues with at least 80% conservation are shown as sticks. Those residues analyzed by mutagenesis are indicated with blue labels. (D) EMSA of the yU3BC RNA with the mutant Rrp9 WD domains. The 5′-32P-labeled yU3BC RNA was incubated with the Rrp9 WD domain of indicated concentrations in the absence or presence of 100 nM Snu13. (E) Yeast growth assay of rrp9 mutants. The rrp9Δ strain complemented by wild-type (WT) RRP9 on a URA3 plasmid was transformed with a LEU2 vector encoding WT or mutant Rrp9. Fivefold serial dilutions of yeast cells were grown at 30°C on synthetic complete (SC) medium with or without 5-FOA, which counter-selects the URA3 plasmid carrying WT RRP9. DE2A is the D353A and E354A double mutant. 3K3A is the K429A, K430A, and K431A triple mutant. RW2D is the R515D and W552 double mutant. M5 is a combination of Y319D, ED2A, 3K3A, and RW2D.