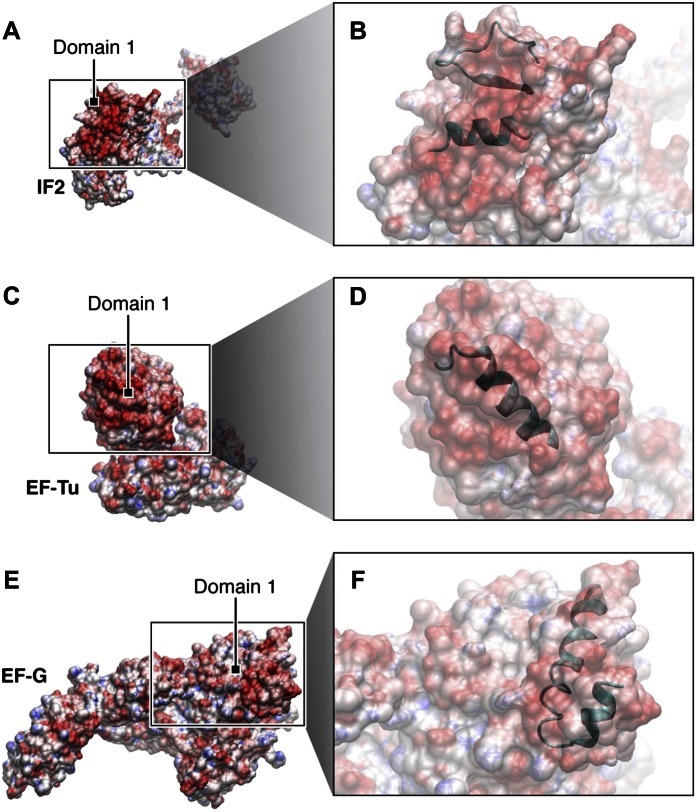
Figure 10. Electrostatic surface potentials of L12-CTD, RF3 and other major translational GTPases.
Red surfaces are electronegative, blue surfaces electropositive. (A) The electrostatic surface potential of RF3 (B) Close-up of domain 1 in RF3, displaying the position of helix α7 in the G’ subdomain responsible for binding to L12-CTD ([C]; close-up in [D]). The overall surface potential of the G’ subdomain in RF3 is negative and the overall surface charge of helices α4 and α5 in L12-CTD is positive. Figure 10—figure supplement 1: Surface potentials of IF2 (A) and (B), EF-Tu (C) and (D), and EF-G (E) and (F) are all electronegative in domain 1.