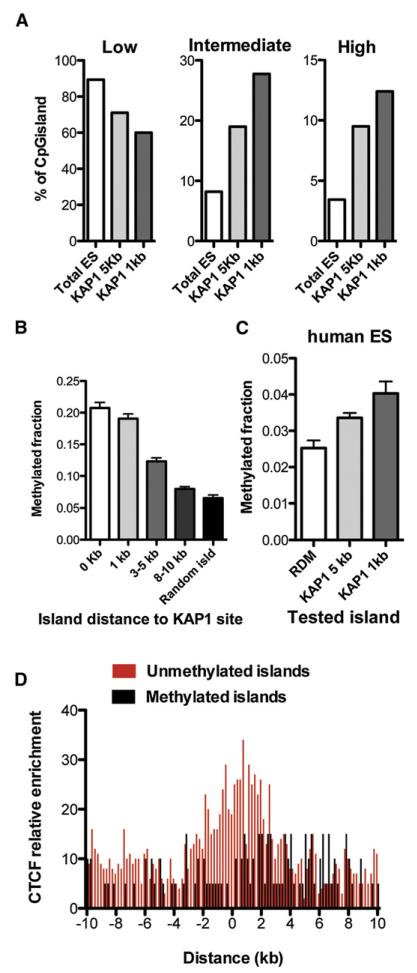
Figure 3. Short-Range Spreading of KRAB/KAP1-Associated DNA Methylation.
(A) Distribution of CpG islands among groups exhibiting low (<20%), intermediate (>20%, <80%) and high (>80%) levels of methylation, their entire pool (Total ES) compared with the subsets located 5 kb and 1 kb from KAP1-binding sites in murine ESCs.
(B) Methylation levels of CpG islands in mouse ESCs, according to distance from KAP1-binding sites. Fischer’s exact test shows significance (p < 0.001) until 8–10 kb (225–532 islands considered per group).
(C) KAP1-close CpG islands (n = 758 for 5 kb and n = 224 for 1 kb) also exhibit higher methylation levels in human ESCs (RDM, randomly selected islands). Measured methylation levels are lower than in murine ESCs due to the use of RRBS (as opposed to full-genome sequencing).
(D) Anticorrelation of CTCF enrichment and DNA methylation on KAP1-close CpG islands in murine ESCs. The 0 kb point represents the middle of the distance between KAP1-binding sites and CpG islands, restricting this in silico analysis to islands situated 5 kb or less from a KAP1 site.