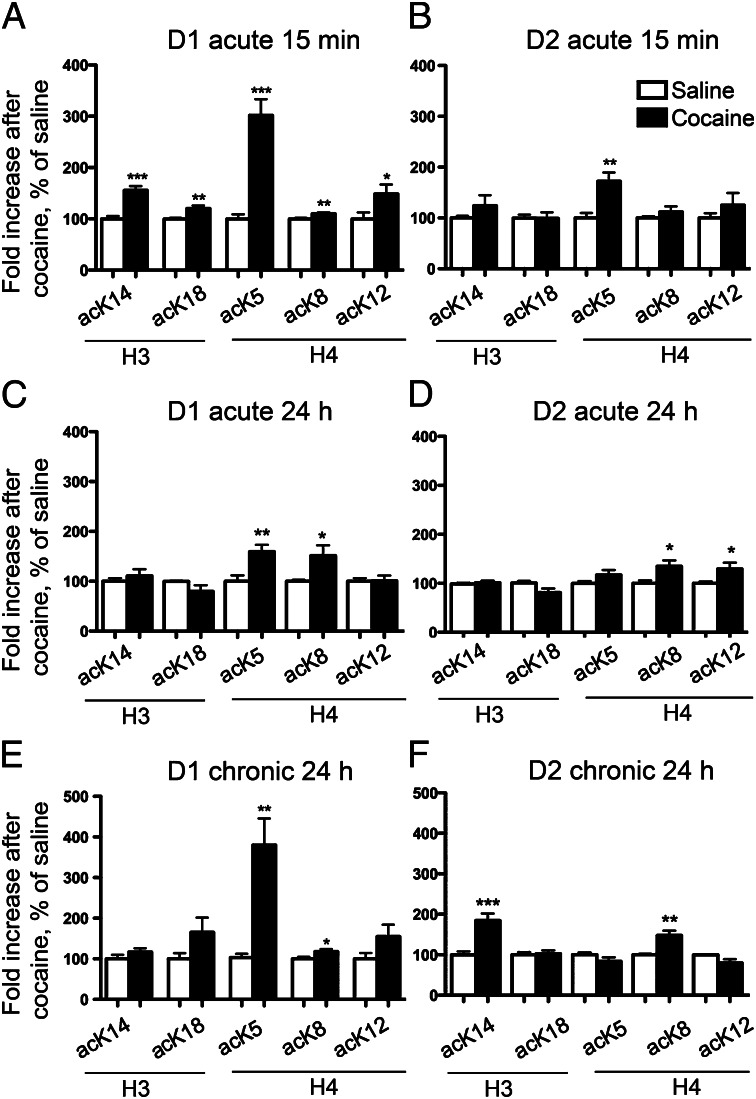
Fig. 4.
Acute and chronic cocaine administration induces distinct patterns of histone H3 and H4 acetylation in D1 and D2 nuclei. Flow cytometry analysis of H3 acetyl-lysine14 (acK14) and acetyl-lysine18 (acK18), and of H4 acetyl-lysine5 (acK5), acetyl-lysine8 (acK8), and acetyl-lysine12 (acK12) fluorescence in the GFP-positive nuclear fraction from D1 (A, C, and E) or D2 (B, D, and F) neurons. EGFP–L10a mice were injected with saline or cocaine (20 mg/kg) and killed 15 min (A and B) or 24 h (C and D) later. Other mice received a daily injection of 20 mg/kg cocaine or saline for 7 d and were killed 24 h after the last injection (E and F). Quantification of flow cytometry data are represented as percentage of saline-treated controls, mean + SEM (n = 8–14; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, Student t test).