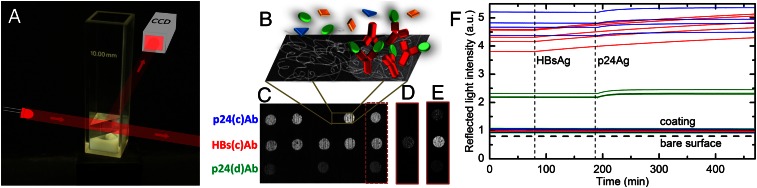
Fig. 1.
Optical setup and measured intensity of reflected light. (A) A standard 1-cm cuvette containing a prism of Hyflon AD is shown. The diagonal face of the prism has been functionalized with DMA-NAS-MAPS copolymer and spotted antibodies. The prism is held by a plastic support that also houses a stirring magnetic bar. The light emitted by a LED is reflected by the sensing surface and acquired by a CCD camera. The temperature of the cuvette is maintained at 37 °C ± 0.1 °C. (B) Schematic illustration of the functionalized surface showing the copolymer as gray threads, the immobilized antibodies, and the target molecules, some of them bound to antibodies. (C) Image of the light reflected by the prism surface spotted with antibodies targeting proteins HBsAg and p24Ag acquired before the addition of the antigens in solution. Multiple spots of the same antibody are placed in the same row, as shown. The image of the three spots on the right-hand side of C is subtracted from the image of the same area acquired 110 min after the addition of 50 ng/mL HBsAg in solution and 280 min after the subsequent addition of 50 ng/mL p24Ag. The resulting brightened images are, respectively, shown in D and E. (F) Reflected light intensity of the spots of HBs(c)Ab (red), p24(c)Ab (blue), and p24(d)Ab (green) shown in C, measured before and after the addition of the corresponding target molecules in solution (injection times are indicated by the vertical dashed lines). The colored lines around the unit value of reflected light represent the intensity of the copolymer-coated surface around each spot. The horizontal dashed line at the bottom indicates the intensity of light reflected by the bare surface.