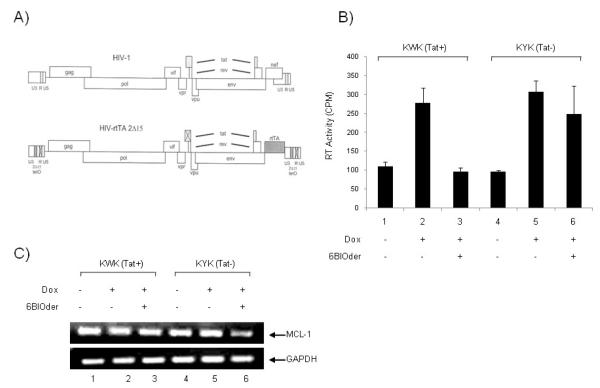
Figure 7. Effect of BIOder in dox-dependent HIV-1 variants in macrophages.
A) HIV-1 genome and modifications that were introduced to construct HIV-rtTA. In brief, TAR-Tat transcriptional axis was replaced by the tetracycline-inducible tetO-rtTA system. Inactivation of TAR and Tat is indicated by crosses through the motifs (Verhoef et al., 2001). B) The pLAI chimera plasmids, KWK and KYK (20 μg), were individually transfected (electroporation) into the differentiated macrophages (~4 × 106) using 250 nM PMA for three days. The culture was maintained with dox (1,000 ng/ml) and BIOder (50 nM), and virus replication was monitored by measuring the amount of RT produced in the culture medium at day 10. No virus replication was observed in the absence of dox, indicating that replication is strictly dependent on the inserted Tet system. C) Macrophages were treated and transfected as described above in B. On day 10, cell pellets were lysed in Buffer RLT and RNA extracted by Qiagen’s RNeasy kit. RNA was treated with 0.25 mg/ml DNase I at 37°C for 1 hour, followed by heat inactivation at 65°C for 15 minutes. A total of 30 ng of total RNA was used to generate cDNA with the iScript cDNA Synthesis kit using random primers. PCR was performed with GAPDH and MCl-1 specific primers.