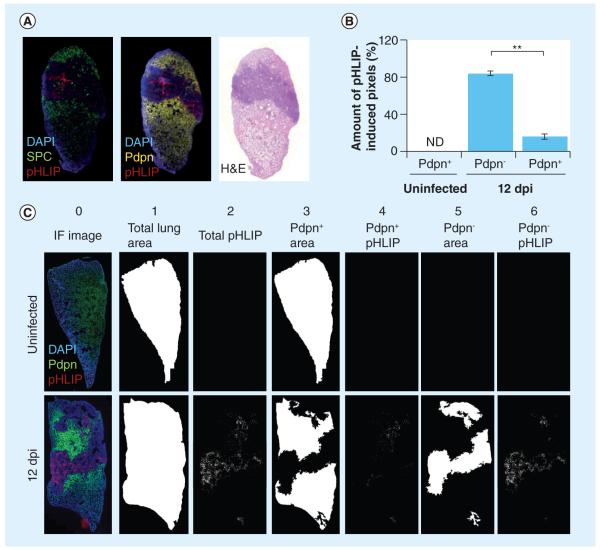
Figure 5. pH (low) insertion peptide targets damaged lung tissue.
(A) pHLIP targets damaged lung tissue devoid of normal alveolar type I (ATI) and alveolar type II (ATII) cells. Representative images of lungs sections stained with anti-SPC and anti-Pdpn. pHLIP (red) does not colocalize with SPC+ ATII (green) or Pdpn+ ATI cells (yellow). (B) pHLIP is mostly observed in regions devoid of Pdpn+ ATI cells. The percentages of pHLIP+ pixels in Pdpn+ and Pdpn− regions were calculated using two lung sections per mouse (n = 3). There are significantly more pHLIP-induced pixels in Pdpn− regions (84.1 ± 2.7%) compared with Pdpn+ regions (15.9 ± 2.7%) of influenza A/Puerto Rico/8/34-infected mice. Bars indicate standard error of the mean. (C) Coincidence of pHLIP+ regions and Pdpn+ and Pdpn− regions. Total area of lung sections (column 1) according to DAPI staining (column 0). Pdpn+ areas (column 3) and Pdpn− areas (column 5) were imaged and quantified according to Pdpn immunohistochemistry. Total pHLIP staining is shown in column 2 and pHLIP staining that coincides with Pdpn+ or Pdpn− regions are shown in columns 4 and 6, respectively.
**p < 0.01 (Student’s t-test).
dpi: Days postinfection; H&E: Hematoxylin and eosin; IF: Immunofluorescence; ND: Not determined; Pdpn: Podoplanin; pHLIP: pH (low) insertion peptide; SPC: Surfactant protein C.