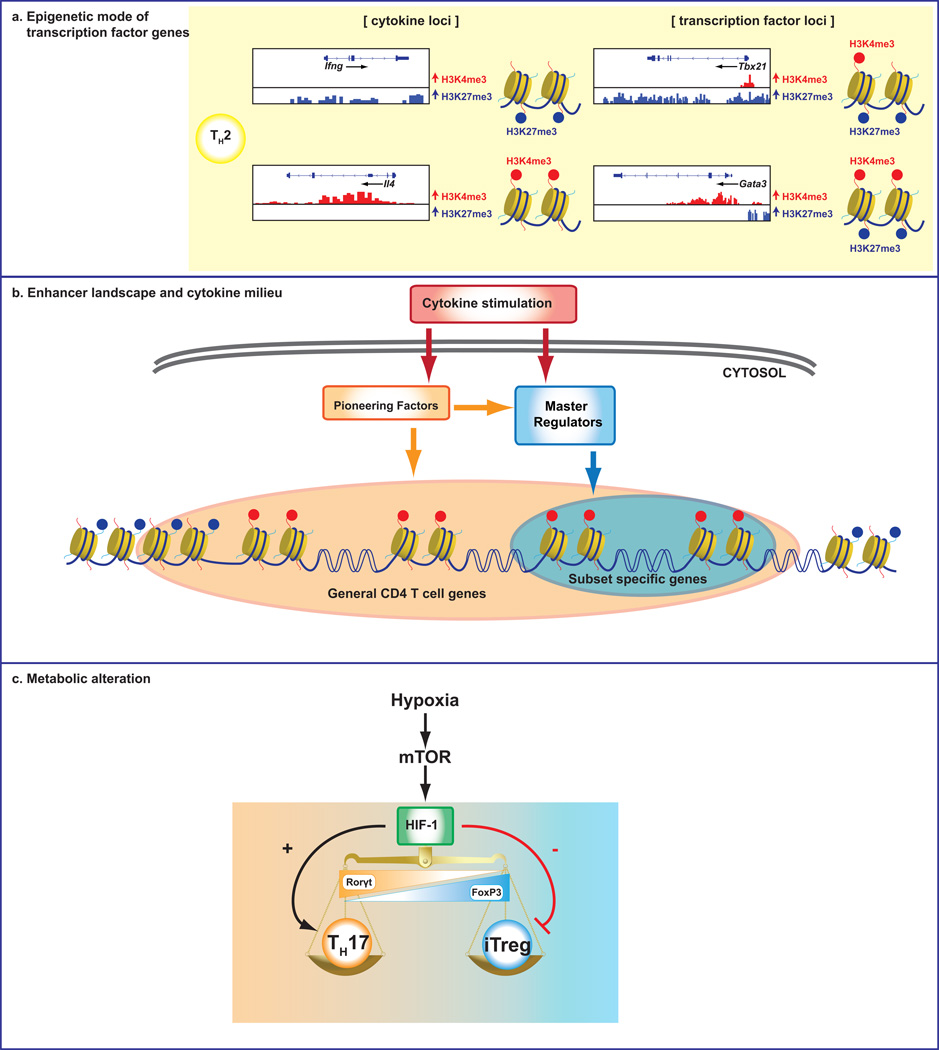
Fig 3. Mechanisms underlying plasticity of Helper T cells.
(a) Specific modifications of the histone molecules that make up the nucleosomes are associated with accessibility. (b) Cytokine milieu can induce “pioneering factors” and activate different STATs, which are indispensable for establishing the genomic epigenetic landscapes of developing helper T cells and dictating the accessibility of key target genes. Master regulators may be better viewed as critical modulators, but not drivers of the chromatin architecture underlying helper cell identity. (c) Alterations in T cell metabolism also have critical roles in the plasticity of helper T cell lineages.