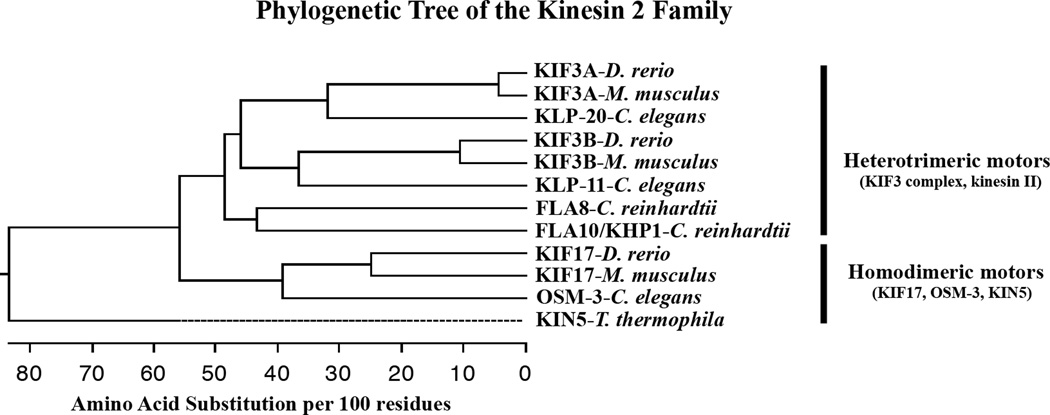
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree showing the relationship of kinesin 2 family heavy chains discussed in this review. The tree was constructed with the Clustal W method of multi-sequence alignment using DNASTAR software. A more complete analysis of all kinesin heavy chains including the kinesin 2 family can be seen in [6] and the associated website. The tree shows evolutionary distance measured as substitutions per 100 amino acids using the full-length sequences of each heavy chain. Included are the heterotrimeric heavy chains KIF3A and KIF3B from Danio rerio and Mus musculus. The comparable heavy chains, KLP-20 and KLP-11, from Caenorhabditis elegans, and FLA10/KHP1 and FLA8 from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are included as well. FLA8 is the heavy chain binding partner of FLA10 [58]. The homodimeric heavy chains include KIF17 from D. rerio and M. musculus, OSM-3 from C. elegans, and KIN5 from Tetrahymena thermophila. The dashed line associated with KIN5 represents a negative branch length caused by averaging during the alignment. A homodimeric kinesin 2 motor has not been described in C. reinhardtii.