Figure 2.
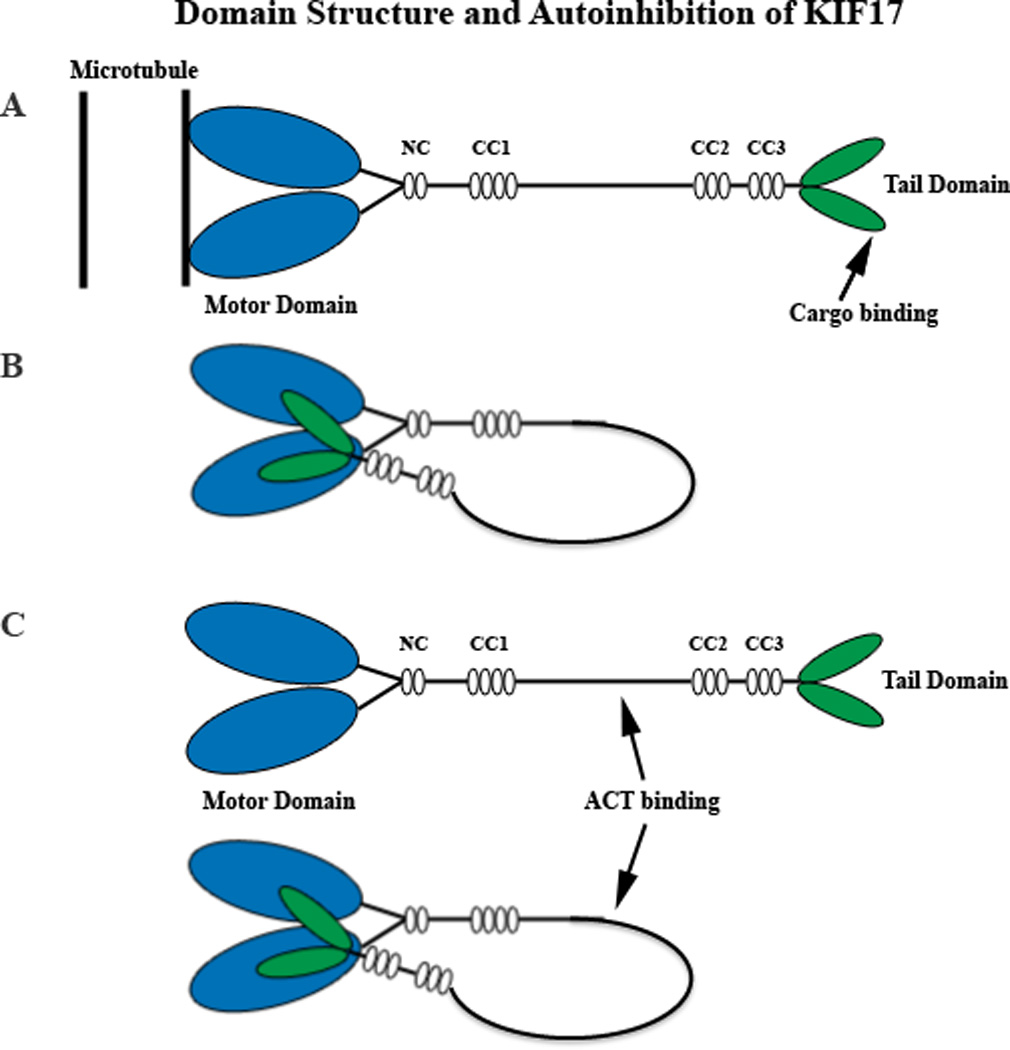
Diagrammatic representation of the KIF17 homodimer in its active (A) and auto-inhibited (B) configurations. In B, the cargo binding tail domain (green) associates with the microtubule binding ATPase head domain (blue). Cargo binding could involve intermediate adaptor complexes, as in the case of NR2B trafficking in dendrites or IFT trafficking in cilia. However, in the testis, ACT binds to an intermediate domain (C) within the stalk rather than the tail in a regulatory event that occurs independently of KIF17 motor activity and microtubules. The structural configuration of KIF17 for ACT binding is not known, but in theory could occur in either the extended or auto-inhibited configuration. Not drawn to scale. CC, coiled-coil domains 1, 2, and 3; NC, neck coil domain.
