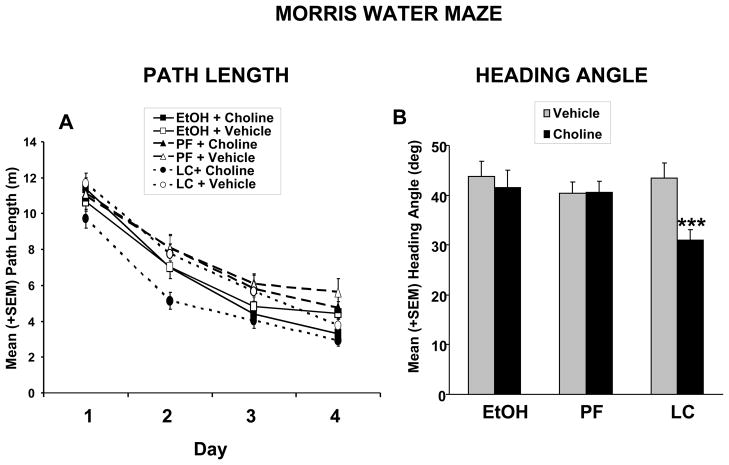
Figure 2.
(A) Mean (+ SEM) path length to find the platform in the Morris Water Maze task over testing days. Prenatal alcohol exposure did not significantly affect acquisition, although PF subjects were significantly impaired compared to both EtOH and LC subjects. Choline supplementation improved spatial learning performance among LC controls, producing a significant effect of choline. (B) Mean (+ SEM) heading angle (chosen path compared to direct path to platform) during Morris water maze acquisition. Choline supplementation significantly improved performance accuracy in LC, but not EtOH or PF subjects, producing a significant of choline. No significant effect of ethanol was found.
***= significantly different from all other groups