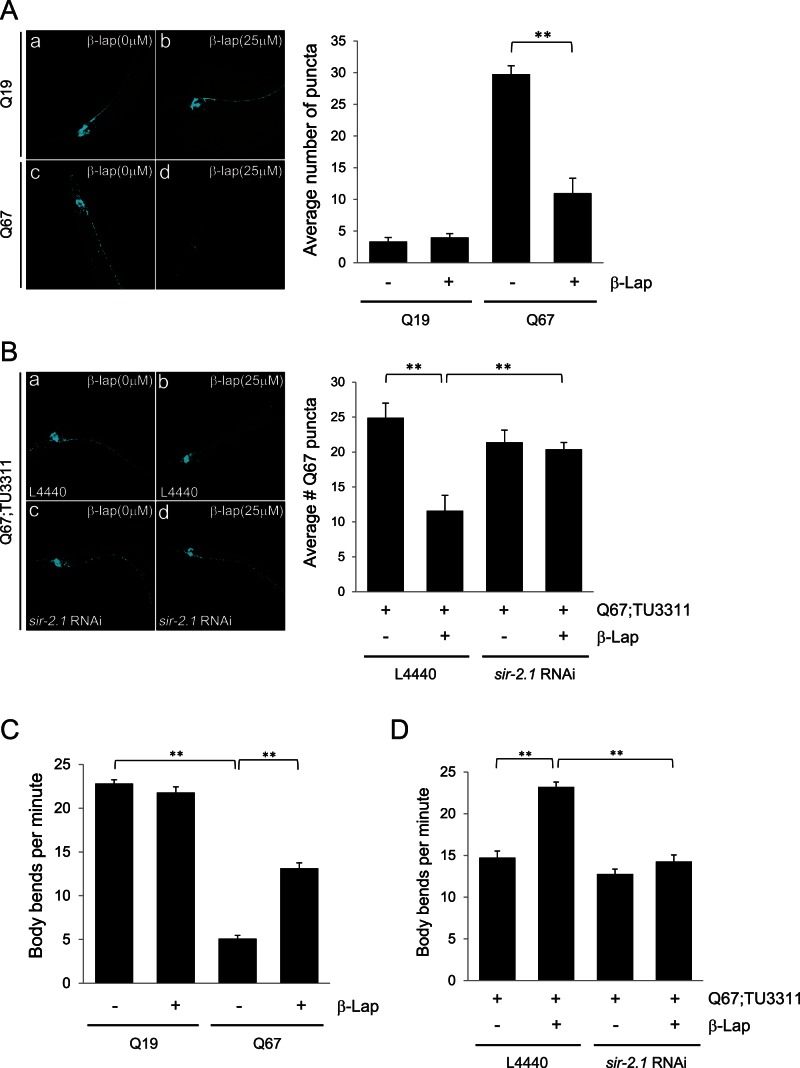
Figure 4. β-lap protects polyQ-expressing neurons from toxicity in C. elegans.
A and C. Fluorescence micrographs of Q19- (a and b) and Q67-expressing C. elegans (c and d) are shown in the presence (b and d) and absence (a and c) of 25 µM β-lap. All animals depicted are young adults (4 days post-hatch). The average number of polyQ puncta (A) and body bends during 1 min of continuous movement on agar plates (C) were quantified and plotted. Each bar and error bar represents the mean ± SD (A: n = 10, C: n = 31); **p<0.01 (Student’s t-test). B and D. RNA interference experiments using sir-2.1 RNAi in Q67;TU3311 double transgenic worms were performed in the presence (b and d) or absence (a and c) of 25 µM β-lap. The average number of polyQ puncta (B) and body bends during 1 min of continuous movement on agar plates (D) were quantified and plotted. Each bar and error bar represents the mean ± SD (A: n = 10, C: n = 31); **p<0.01 (Student’s t test).