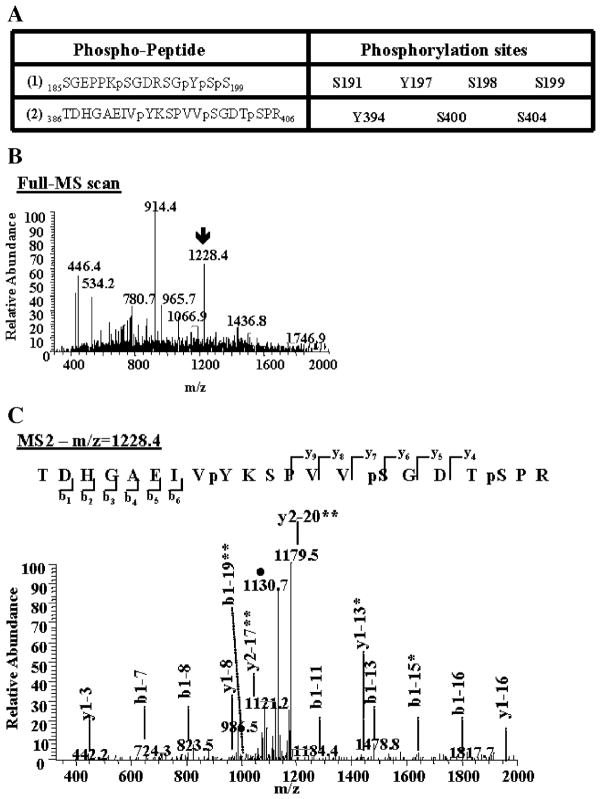
Fig. 4.
Identification of novel tyrosine phosphorylation sites on tau proteins. Immunoprecipitated tau proteins were digested with trypsin. The peptides produced were resolved by reverse-phase chromatography on line with nano-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (MS) and analyzed as described in Materials and methods. (A) Two phospho-peptides containing phosphorylated tyrosine (Y) were identified. These phospho-peptides contain other known and unknown serine (S) phosphorylated sites. The amino acid number corresponds to its position in the longest tau isoform peptide sequence (2N4R). (B) The arrow on the MS spectrum points toward the doubly charged ion corresponding to phospho-peptide (2). (C) This precursor ion was then selected and subjected to fragmentation (MS2), generating b and y product ions that represent specific fragments used for identification of the peptide sequence and phosphorylation sites. The filled circle (●) denotes a doubly charged ion containing the neutral loss of 98 amu corresponding to the lost of the two phosphate groups attached to the serine residues on the phospho-peptide (2). One asterisk indicates b or y ions containing the neutral loss of the phosphate groups. Two asterisks denote a doubly charged b or y product ions.