Figure 5. Persistent spiking did not appear in vivo under urethane anaesthesia.
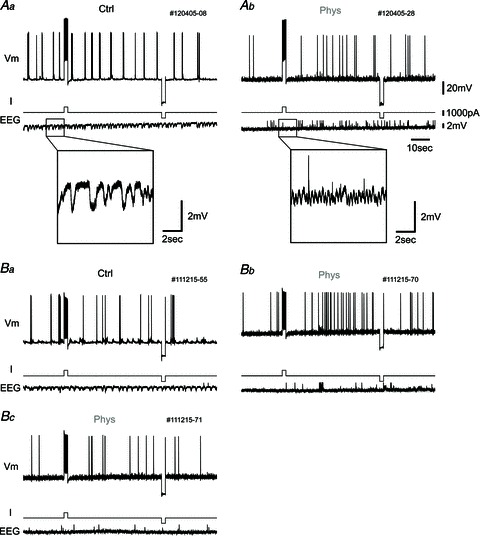
A, one example of the response to current pulse injection. Top traces, membrane potential (Vm); middle traces, injected current (I); and bottom traces, hippocampal EEG (EEG). Aa, in this protocol, membrane potential is first set slightly below the level of constant spike firing by changing the injected current. Then, a 1000 pA, 2 s current pulse is injected to elicit persistent firing after the cessation of current stimulation. After the waiting period (50 s), a 2 s negative current pulse (−1000 pA) is injected to eliminate any remaining effect of the positive current pulse. The hippocampal EEG shows slow-wave activity in the control condition (inset, higher magnification). Ab, in the presence of physostigmine, persistent spiking does not occur after current pulse injection. The hippocampal EEG shows fast-wave activity due to physostigmine administration (inset, higher magnification). B, another example of the response to current pulse injection with picrotoxin in the recording pipette. Ba, there is no change of spiking in control condition. Bb, after physostigmine application, the cell tends to increase firing rate after the positive current pulse in this case, but does not show continuous persistent spiking. Bc, this is the response of the same neuron with the same current injection protocol as shown in Bb, but the neuron does not show an increase in firing frequency again.
