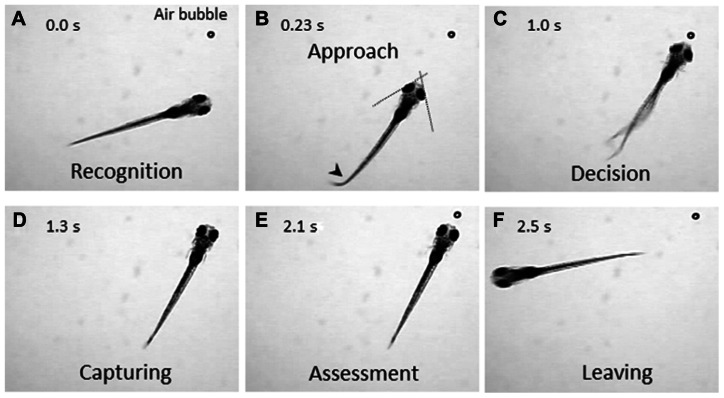
FIGURE 1.
Prey-capture behavior can be divided into multiple steps of actions. A 7-day postfertilization (dpf) larva reacts to an air bubble. A possible cognitive or motor process is assigned to each action. (A) Recognition: An object (an air bubble) comes into sight of a larva and recognized. (B) Approach: The larva orients its body toward the object with eye convergence (indicated by two crossed dotted lines). An arrowhead indicates J-turn. (C) Decision-making: The larva makes the final decision to catch the object or abort the behavior. (D) Capturing: The larva successfully captures the object and put it into the mouth. (E) Assessment: The larva spits the air bubble out because it is not food. (F) Leaving: The larva leaves the air bubble to explore other areas.