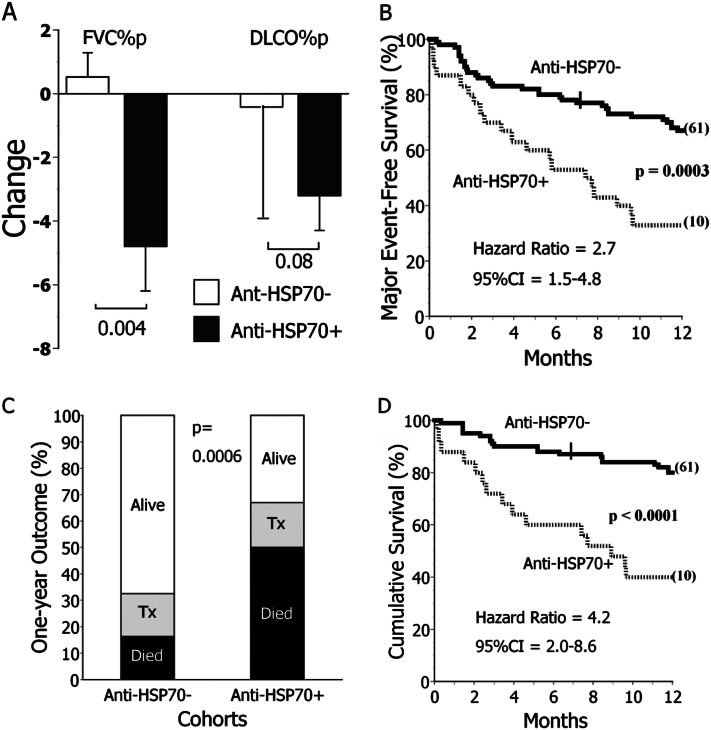
Figure 4.
Clinical correlates of heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) autoreactivity determined by immunoblot (IB). (A) Surviving subjects with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) with anti-HSP70 autoantibodies detected on IB testing (anti-HSP70+) (n = 14) had greater subsequent decrements of FVC, as % predicted values (FVC%p), and an insignificant tendency for greater decrements of percent predicted diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DlCO%p), compared with the subjects without this autoantibody (anti-HSP70−, n = 59). Pulmonary function determinations were made approximately 6 months after the plasma sample acquisitions (see text). (B) Patients with IPF with anti-HSP70 autoantibodies detected by IB (n = 30) had worse prognoses than those who were autoantibody negative (n = 92). Major (adverse) events are defined as either deaths or lung transplantations. Cross hatches denote censored events, and numbers in parentheses denote subjects censored at the end of observation. (C) The proportion of subjects with IPF who died during the next year was threefold greater among those with anti-HSP70 autoantibodies (anti-HSP70+) compared with the anti-HSP70−. Tx = transplanted. (D) Among patients with IPF who did not have lung transplantations during the observation period, those with anti-HSP70 autoantibodies (n = 25) had worse prognoses than the autoantibody-negative subpopulation (n = 77). CI = confidence interval.