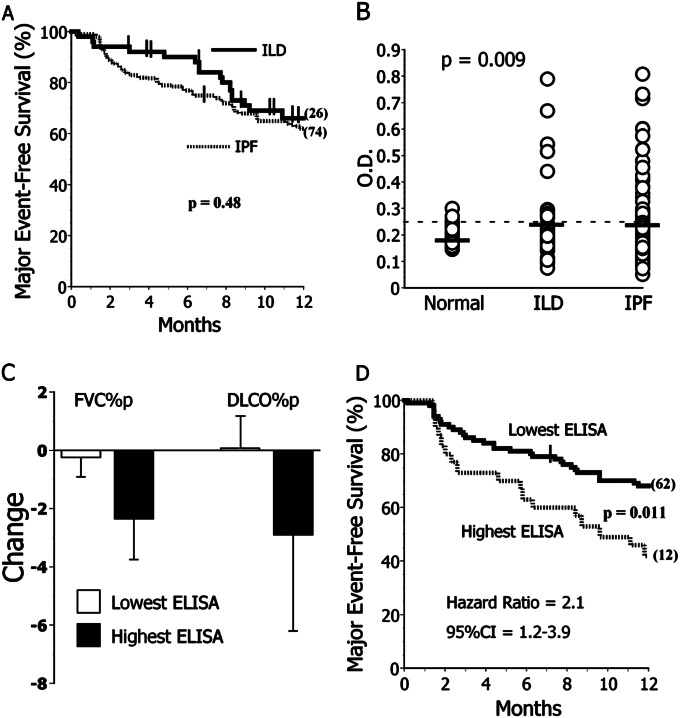
Figure 5.
Heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) autoreactivity determined by ELISA. (A) Outcomes were near identical among subjects with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) (n = 121) and non-IPF interstitial lung disease (ILD) (n = 51). Post hoc analyses of absolute 1-year survival limited to those subjects who did not have transplantations during the observation period were also similar among these experimental cohorts (74 ± 4% vs. 78 ± 7% for IPF and ILD, respectively; P = 0.62). (B) Anti-HSP70 IgG ELISA optical density (OD) values were near identical in subjects with IPF and subjects with non-IPF ILD, and both were greater than among healthy control subjects (n = 59). The P value here is per Kruskal-Wallis (three-group) comparison. Values for both IPF and ILD were significantly greater than normal subjects in post hoc two-group analyses using Mann-Whitney tests. The dashed line denotes the mean plus SD of the values in normal subjects here. Thick horizontal lines denote the mean of each subpopulation. (C) Subjects with IPF with anti-HSP70 ELISA OD in the highest quartile (Highest ELISA) had nonsignificant trends for greater subsequent (∼ 6-mo) decrements of FVC % predicted (FVC%p) and percent predicted diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DlCO%p). (D) Subjects with IPF in the highest quartile of anti-HSP70 ELISA OD values (Highest ELISA) more frequently had major adverse events (deaths or lung transplantations) during the year after their specimen acquisitions. In contrast, anti-HSP70 autoantibody measures had no associations with clinical manifestations in the non-IPF ILD disease control cohort (see online supplement E3). CI = confidence interval.