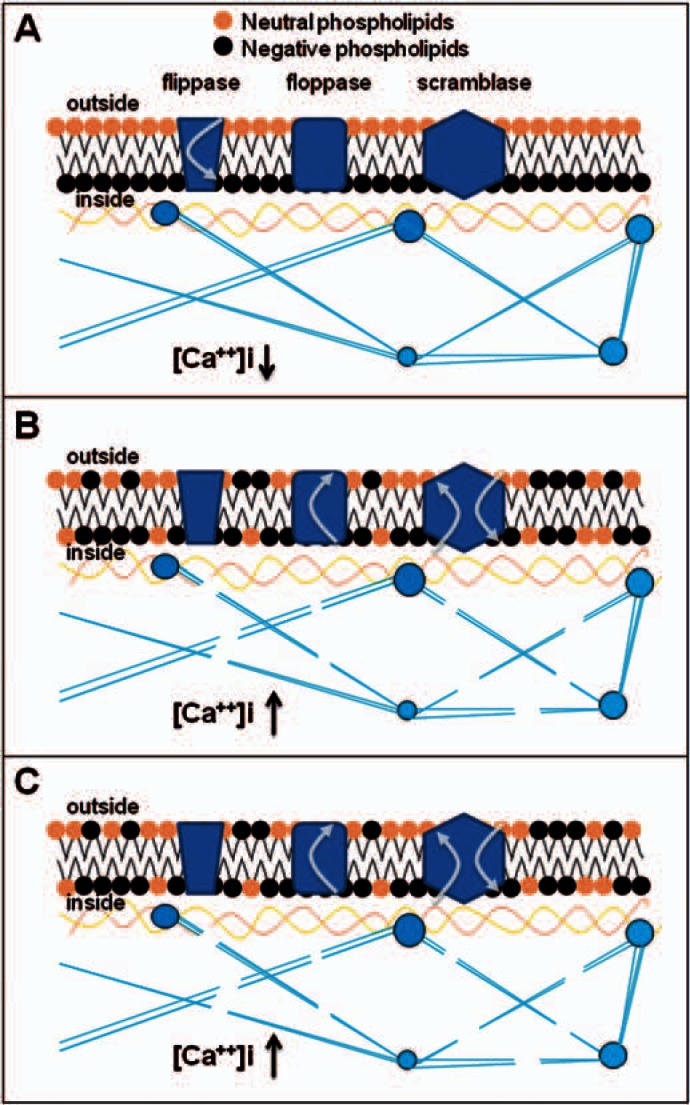
Fig. 1.
Model of formation of microparticles. A Phospholipid organization is under the control of 3 enzymes: flippase, floppase, and scramblase. In resting cells, flippase internalizes negatively charged phospholipids and maintains the asymmetry of the phospholipid bilayer. Floppase and scramblase are inactive, and the cytoplasm calcium concentration is low. B Upon activation, intracellular calcium concentration increases, flippase is inhibited, while floppase and scramblase are activated. Floppase externalizes phosphatidylserine, a negative phospholipid, and scramblase translocates phospholipids non-specifically through the membrane resulting in the loss of phospholipid asymmetry. C Increased intracellular calcium also activates proteases that cleave the cytoskeleton; the membrane is less rigid and can bleb until formation and release of vesicles.