Fig. 3.
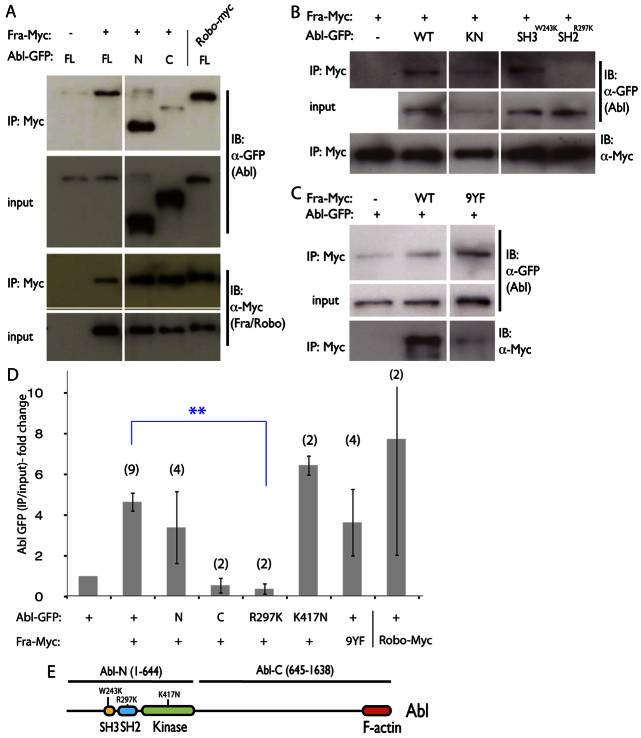
Abl binds to Fra through its N-terminal SH2 motif. (A-C) Co-immunoprecipitation of GFP-Abl fusions expressed in S2R+ cells with anti-Myc antibodies. Western blots representative of at least three independent experiments are shown. Mouse-anti GFP and Mouse anti-Myc (indicated on the right) were used. Constructs are indicated at the top. (A) Abl-FL and Abl-N, but not Abl-C, bind to Fra (compare lanes 2 and 3 to lane 4). Positive control (lane 5) shows that Abl binds Robo-myc. (B) AblR297KGFP does not bind to Fra (lane 5). (C) Tyrosine phosphorylation of Fra is not required for the Abl-Fra interaction, as Fra-9YF pulls down Abl-GFP (lane 3). (D) Quantification of co-immunoprecipitation experiments. Shown are the ratio of immunoprecipitated Abl-GFP to input, normalized to the control (Abl-GFP alone). Number of experiments used for quantification are shown in parentheses. **P<0.01. Error bars indicate s.e.m. (E) Schematic depicting Abl indicating relevant features. Mutations and truncations used in this figure are labeled.