Figure 4.
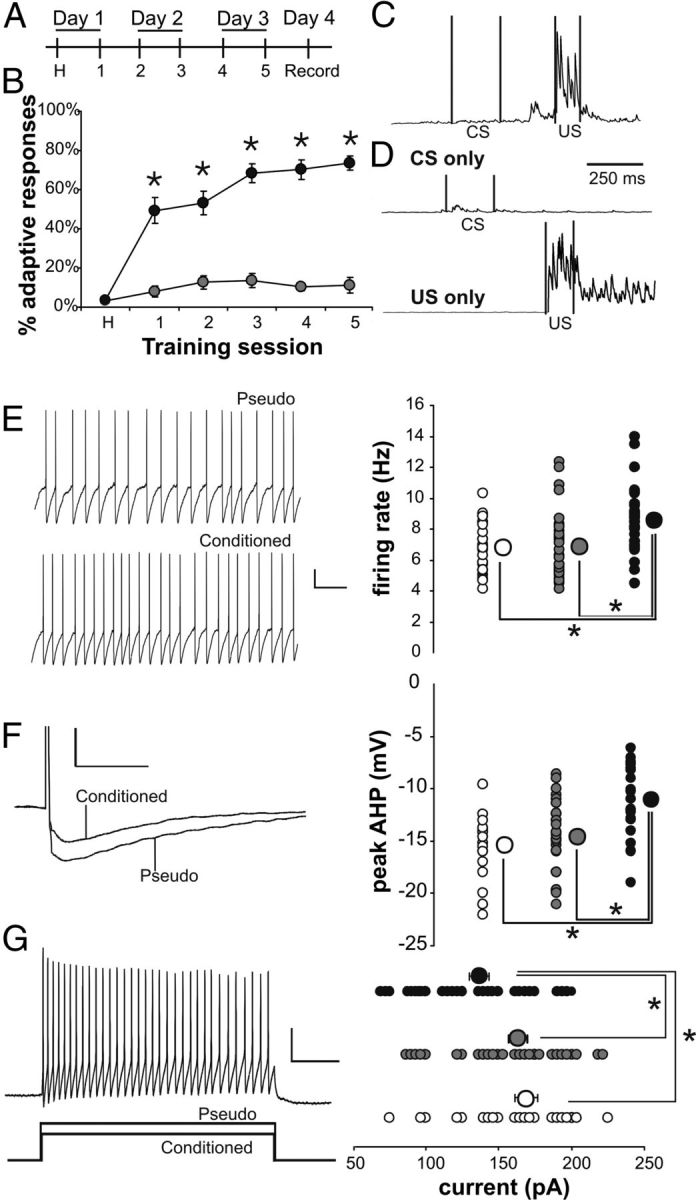
Intrinsic excitability is increased in SOMs from trained mice compared with controls. A, Mice were trained twice a day for 3 d, and electrophysiological recordings were made on the fourth day. B, Conditioned mice (closed circles; N = 29) exhibited significantly more adaptive responses compared with pseudoconditioned mice (open circles; N = 24) (rmANOVA: F(1,51) = 117.4, p < 0.0001; *unpaired t test p < 0.01). C, D, Examples of integrated EMG response are illustrated from a conditioned (C) and a pseudoconditioned (D) mouse. C illustrates an adaptive response to a paired presentation of the whisker vibration (CS) and periorbital shock (US) during session 5. D illustrates the lack of an adaptive response to a CS-alone trial and an US-alone trial from a pseudoconditioned mouse during session 5. E, Learning resulted in significantly increased spontaneous firing rate at resting membrane potential in SOM neurons. Conditioned, black circle; pseudoconditioned, gray circle; naive, open circle. Calibration: 10 mV, 500 ms. F, The AHP following a single action potential is significantly reduced in SOMs from conditioned mice compared with controls. Calibration: 10 mV, 50 ms. G, The current required to elicit 20 action potentials in 1 s was significantly less in cells from conditioned animals compared with controls. Calibration: 20 mV, 150 pA, 200 ms. n: naive 25, pseudo 32, conditioned 32. Note: *Fischer's PLSD p < 0.05. Smaller circles are the data points from individual neurons. Larger circles are the group means. In some instances, the SEM of each group is smaller than the size of the circle that represents the group mean data.
