Figure 5.
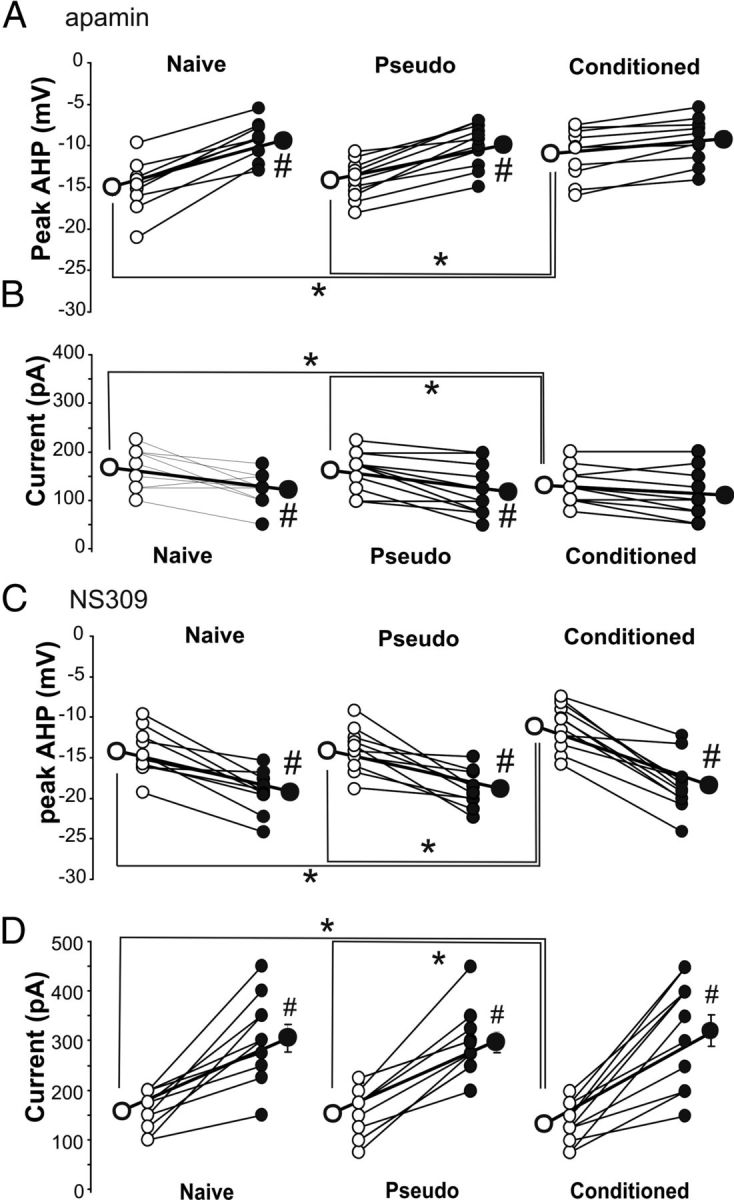
Learning-related increased intrinsic excitability of SOM neurons is mediated by reductions in the apamin-sensitive AHP. A, Repeated ANOVA revealed significant training (F(2,25) = 5.96, p < 0.001) and apamin (F(1,25) = 3.84, p < 0.05) effects on the peak AHP. Before apamin application, the peak AHP was significantly reduced in SOM neurons from conditioned mice (pre-apamin ANOVA: F(2,25) = 5.77, p < 0.01; *Fischer's PLSD p < 0.05). Apamin (500 nm) reduced the AHP following a single action potential in cells from pseudoconditioned and naive animals, but not from conditioned animals (#paired t tests p < 0.05). After apamin there was no difference between groups in the size of the AHP. B, Repeated ANOVA revealed significant training (F(2,25) = 5.76, p < 0.01) and apamin (F(1,25) = 4.17, p < 0.05) effects on the current necessary to elicit 20 action potentials (APs) in 1 s. Before apamin application, significantly less current was needed in SOM neurons from conditioned mice to elicit 20 APs (pre-apamin ANOVA: F(2,25) = 4.00, p < 0.05; *Fischer's PLSD p < 0.05). Apamin (500 nm) decreased the amount of current required to elicit 20 APs in cells from pseudoconditioned and naive animals, but not from conditioned animals (#paired t tests p < 0.05). After apamin, there was no difference between groups in the degree of accommodation. n: naive 9, pseudo 10, conditioned 10. C, Repeated ANOVA revealed significant training (F(2,25) = 4.22, p < 0.05) and NS309 (F(1,25) = 4.59, p < 0.05) effects on the peak AHP. Before NS309 application, the peak AHP was significantly reduced in SOM neurons from conditioned mice (pre-NS309 ANOVA: F(2,25) = 3.45, p < 0.05; *Fischer's PLSD p < 0.05). Application of 10 μm NS309 increased the size of the AHP in neurons from all training groups (#paired t tests p < 0.005) and abolished the learning-related AHP reduction. D, Repeated ANOVA revealed significant training (F(2,27) = 4.90, p < 0.05) and NS309 (F(1,27) = 4.24, p < 0.05) effects on the current necessary to elicit 20 APs in 1 s. Before 10 μm NS309 application, significantly less current was needed in SOM neurons from conditioned mice to elicit 20 APs (pre-NS309 ANOVA: F(2,27) = 5.27, p < 0.05; *Fischer's PLSD p < 0.05). NS309 (10 μm) increased the amount of current required to elicit 20 APs in neurons from all training groups (#paired t tests p < 0.05). After NS309, there was no difference between groups in the amount of current required to elicit 20 action potentials. n: naive 8, pseudo 11, conditioned 11. Open circle, Predrug; filled circle, postdrug.
