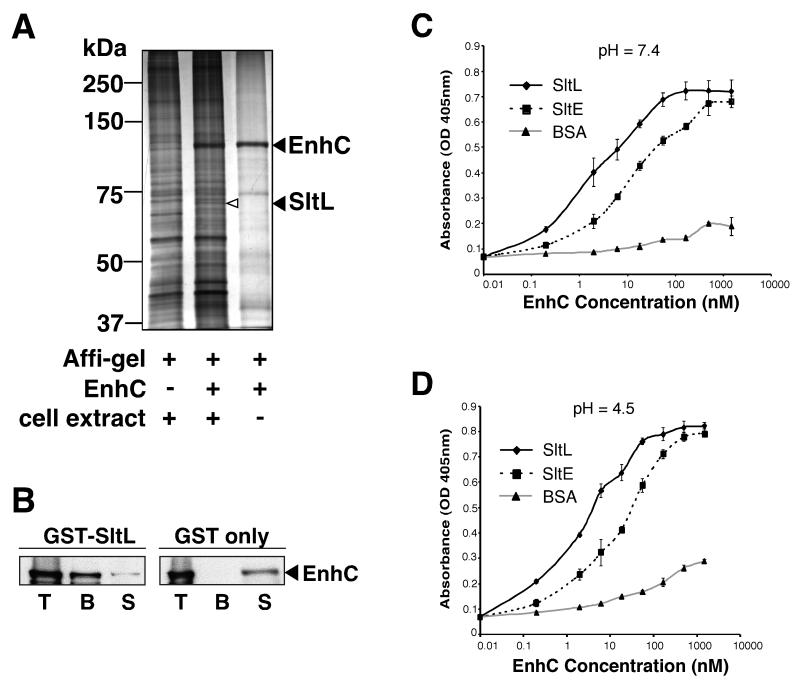
Figure 1. L. pneumophila EnhC directly binds L. pneumophila soluble lytic peptidoglycan transglycosylase (SltL).
(A) SltL specifically binds EnhC-coated beads. Lysates of L. pneumophila were incubated with EnhC-Affigel beads. Bound proteins were released from the beads by boiling in SDS, separated by 10 % SDS-PAGE and visualized by silver staining (Experimental Procedures). Left lane: L. pneumophila extract incubated with control Affigel; Middle lane: L. pneumophila extracts incubated with EnhC-Affigel; Right lane: boiled beads from buffer incubated with Affigel-EnhC. (B) EnhC directly binds SltL. GST-SltL- or GST-Glutathione-Sepharose beads were incubated with purified EnhC and proteins associated with the beads were analyzed by Western blot using anti-EnhC. T: Total input of EnhC; B: EnhC bound to beads; S: EnhC in the supernatant after incubation with beads. (C) EnhC binds L. pneumophila Slt (SltL) with higher affinity than E. coli Slt (SltE). ELISA plates coated with SltL or SltE or BSA were probed with increasing concentrations of EnhC. Shown are mean +/− standard deviation (s.d.) of triplicate wells. The experiment was repeated 3 times. (D). High affinity binding of SltL is maintained at pH = 4.5. Experiment performed exactly as in panel C, probing wells coated with proteins noted in the legend. See also Fig. S1.