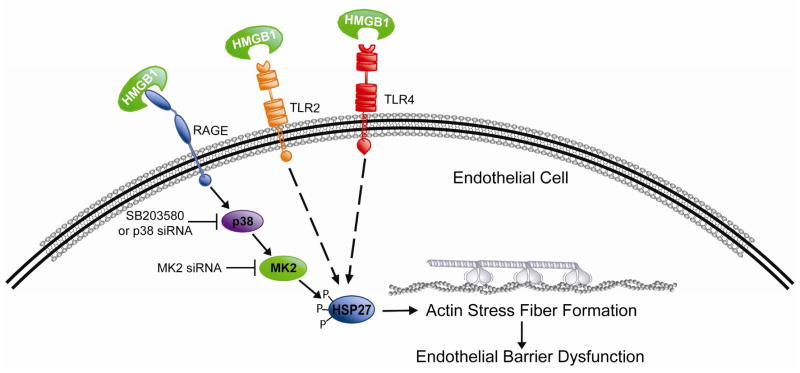
Figure 7. Cartoon schematic of proposed HMGB1 pathway leading to paracellular gap formation and endothelial barrier disruption.
HMGB1 induces EC barrier disruption via ligation of the RAGE receptor, resulting in downstream activation of p38 MAP kinase and MAPKAPK-2, and phosphorylation of the actin-binding protein Hsp27. While RAGE is clearly involved in the functional effect of HMGB1 on TER and paracellular gap formation, TLR2 and TLR4 may also be involved in mediating Hsp27 phosphorylation induced by HMGB1 via mechanisms not yet investigated.