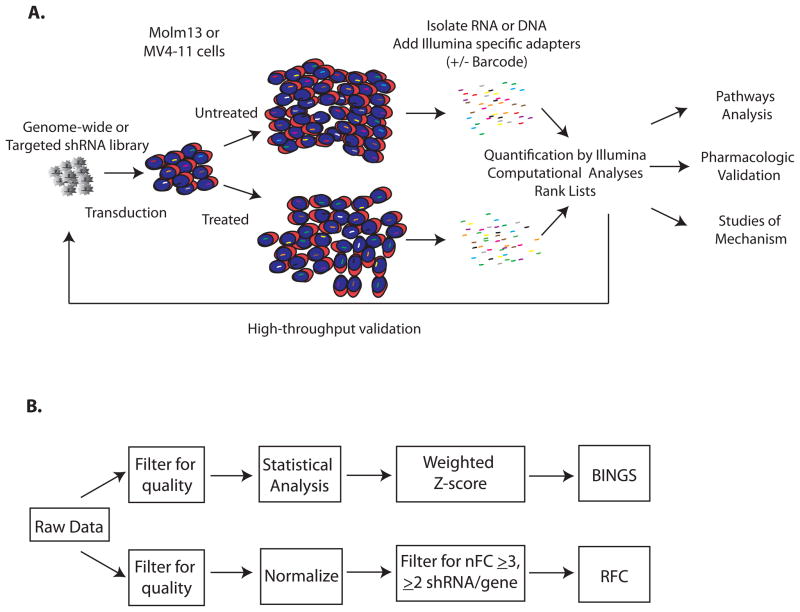
Figure 1. Systematic functional genetic screening.
A. Experimental overview. AML cell lines Molm13 and MV4-11 were transduced with a genome-wide shRNA library and treated with cytarabine at the IC75 dose or left untreated. After recovery in the absence of drug, shRNA tag sequences were isolated and quantified by deep sequencing. Data were analyzed by complementary means generating lists of mediators of chemosensitivity and chemoresistance. A subset of these hits was included in a targeted sub-library for secondary screening. Selected hits were analyzed using Ingenuity Pathways Analysis, validated pharmacologically, and the mechanism of cell fate examined. B. Complementary analyses of differential shRNA tag representation. Data were analyzed by 2 independent processes. The Bioinformatics for Next Generation Sequencing (BINGS) pipeline employed edgeR to identify differentially represented shRNA tags and then applied a weighted z-score to rank genes as providing chemoresistance or chemosensitivity when inhibited (BINGS). A second method takes into consideration the absolute fold-change of normalized shRNA tag counts and redundancy of shRNAs directed against a gene (RFC).