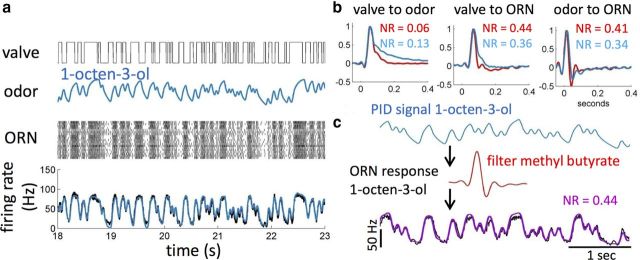
Figure 8.
ab3A response to a slow odor can be predicted using the LN model fitted to the response to methyl butyrate. a, Top to bottom, On–Off state of the valve driving the odor; PID response measured at the fly; and raster plot and PSTH of ab3A response (black, n = 18) and prediction from LN model obtained using the odor-to-ORN filter (blue). Both 1-octen-3-ol and methyl butyrate (Fig. 7) were presented in series on the same neurons. A stimulus sequence was 30 s long with 30 ms correlation time. A recovery time of 3–5 min was allowed between stimulations. b, Linear filters for valve-to-odor, valve-to-ab3A, and odor-to-ab3A transformations for both methyl butyrate (red) and 1-octen-3-ol (blue). c, Prediction (purple) of the measured response of ab3A (black) to 1-octen-3-ol (PID; blue) using the model of ab3A (red) built from the response to methyl butyrate. Odor signal was shifted by 4 ms to take into account the shift in the response function (see also Fig. 9). It was also appropriately normalized to take into account the different gains of the PID and ORN responses to the different odorants.