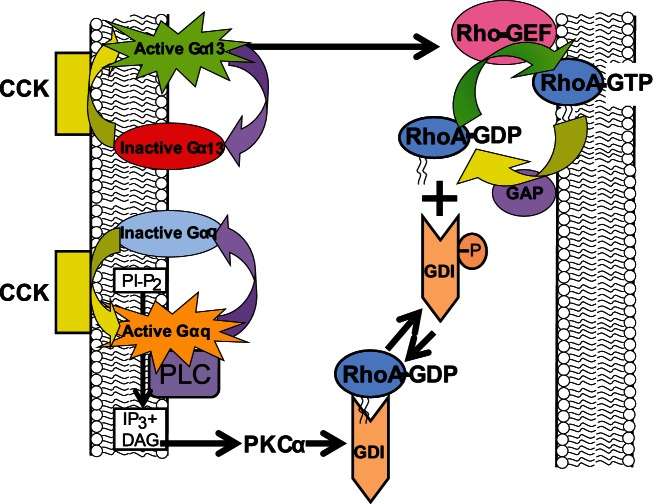
Figure 11. A schematic presentation describing the different signaling components involved in the effect of CCK on RhoA signaling.
Inactive RhoA is localized in the cytosol complexed to RhoGDI1, which masks the geranylgeranylated group. Upon CCK stimulation, two pathways are activated: Gα13 pathway and PKCα pathway. RhoGDI1 is phosphorylated at Ser96 by PKCα, and thereby, releases inactive RhoA. Once inactive RhoA is dissociated, inactive RhoA is able to translocate to membranes and be activated by RhoGEF, in a mechanism which dependent on active Gα13. Finally, GAP inactivates RhoA, which is able to associate with cytosolic RhoGDI1.