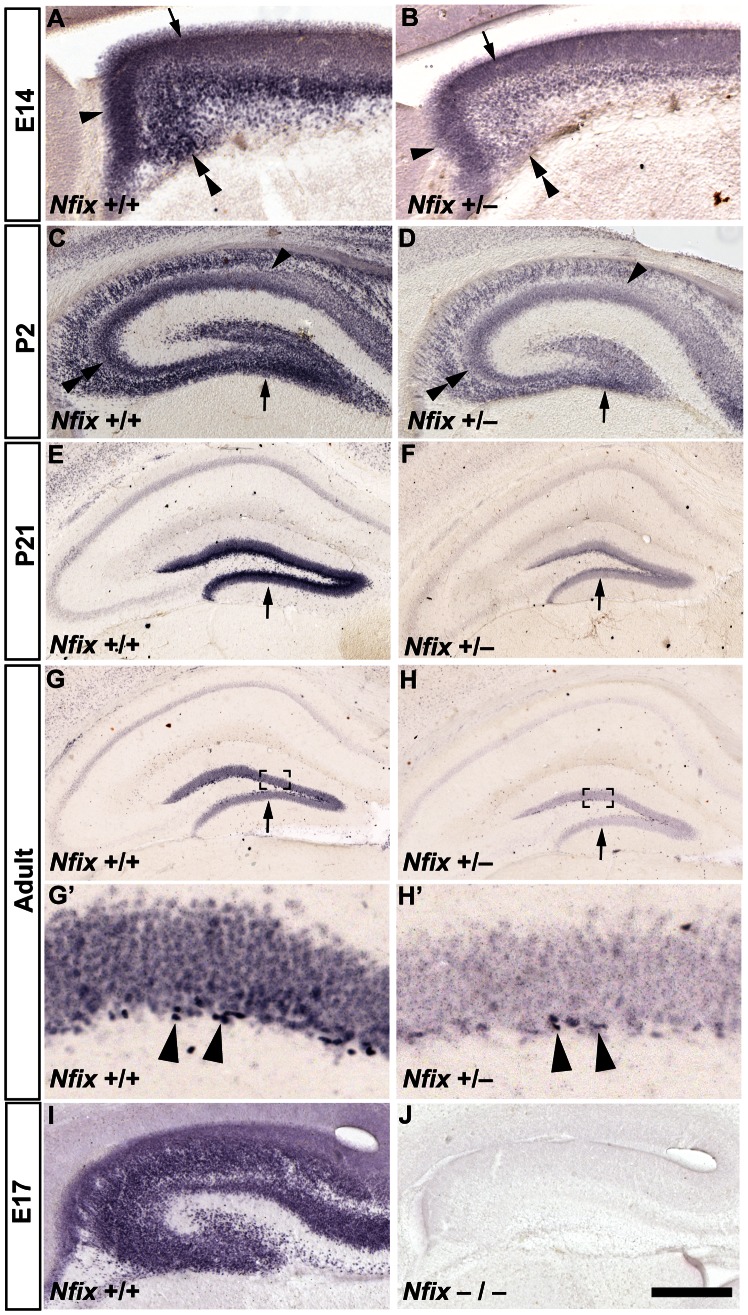
Figure 1. Nfix+/− mice have reduced hippocampal expression of NFIX.
Anti-NFIX staining of wild-type and Nfix +/− coronal brain sections at embryonic, postnatal and adult ages (A–H’). In E14 wild-type mice (A) NFIX was detected within two regions of the hippocampal ventricular zone, the ammonic neuroepithelium (arrow in A) and the dentate neuroepithelium (arrowhead in A), as well as by post-mitotic neurons within the developing hippocampal anlage (double arrowhead in A). At P2, NFIX expression was detected in the wild-type dentate gyrus (arrow in C), CA3 (double arrowhead in C) and CA1 pyramidal cell layers (arrowhead in C) but was detected only in the dentate gyrus at P21 (arrow in E). In adult wild-type mice (G), NFIX was most strongly expressed by cells in the SGZ of the dentate gyrus (arrowheads in G’). The same expression pattern was observed in Nfix +/− mice (B, D, F, H, H’), although the level of NFIX expression was much lower than in wild-type mice at all ages. The specificity of the NFIX antibody is demonstrated by the absence of immunoreactivity in Nfix−/− knockout tissue at E17 (J, compare to panel I). G’ and H’ are magnified views of the boxed regions in G and H respectively. Scale bar (in J): A, B, I, J 150 µm; C, D 250 µm; E, F, G, H 500 µm; G’, H’ 50 µm.