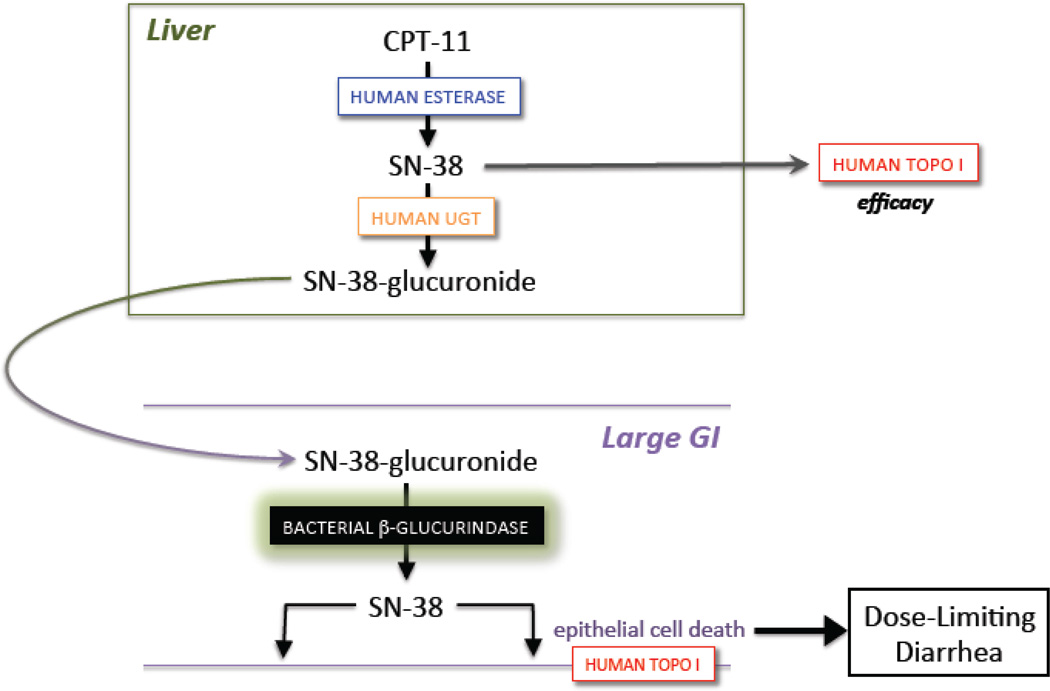
Figure 1.
A. The anticancer drug CPT-11 (Irinotecan) is a prodrug activated to the DNA topoisomerase I poison SN-38 by esterases, and SN-38 is further processed to its SN-38 glucuronide (SN-38G) metabolite by UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) enzymes. Excreted SN-38G is reactivated in the large intestines by bacterial microbiota β-glucuronidase enzymes; lumenal SN-38 contributes to the dose-limiting diarrhea associated with CPT-11 [29]**. B. Potent, selective and non-lethal bacterial β-glucuronidase inhibitors prevent the diarrhea and intestinal damage caused by the reactivation of SN-38G to SN-38 [29]**.