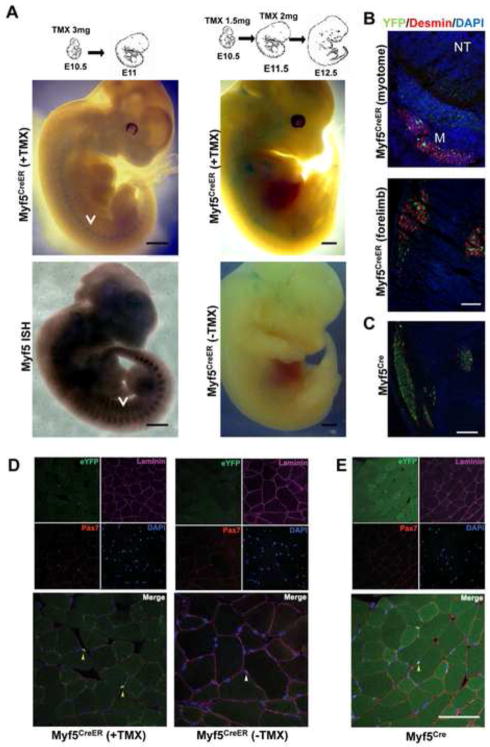
Fig. 2. Characterization of Myf5CreER mice.
(A) Whole-mount Xgal staining of Myf5CreER/wt; R26RLacZ/wt embryos. TMX administration protocols and stages as indicated. Myf5CreER/wt; R26RLacZ/wt embryos injected with corn oil were used as negative controls. Whole-mount in situ hybridization (ISH) of E11.5 embryos with Myf5-specific probes is shown to highlight the pattern of Myf5 expression. Arrows mark the myotomes. Bar, 1 mm. (B) Transverse sections of Myf5CreER/wt; R26RYFP/wt E12.5 embryos treated with TMX (5 mg) at E10.5 and E11.5 were stained with antibodies recognizing YFP and Desmin. DAPI was used to stain the nuclei. YFP+ve cells localize to the myotome (M; Desmin+ve) lateral to the neural tube (NT) and in the forming muscle masses in the forelimbs. Bar, 50 μm. (C) Sections of the limb of E12.5 Myf5Cre/wt; R26RYFP/wt are shown as term of comparison. Bar, 50 μm. (D) Immunofluorescence analysis of skeletal muscle from adult Myf5CreER/wt; R26RYFP/wt mice 2 weeks after TMX injections, or without TMX administration. Bar, 100 μm. (E) Immunofluorescence analysis of skeletal muscle from Myf5Cre; R26RYFP/wt mice. Frozen sections of tibialis anterior muscles were immunostained for YFP, Pax7, and Laminin. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Yellow arrows point to YFP+ve satellite cells (D, E). A white arrow on the merged image shows a YFP−ve satellite cell localized beneath the basal membrane (D).