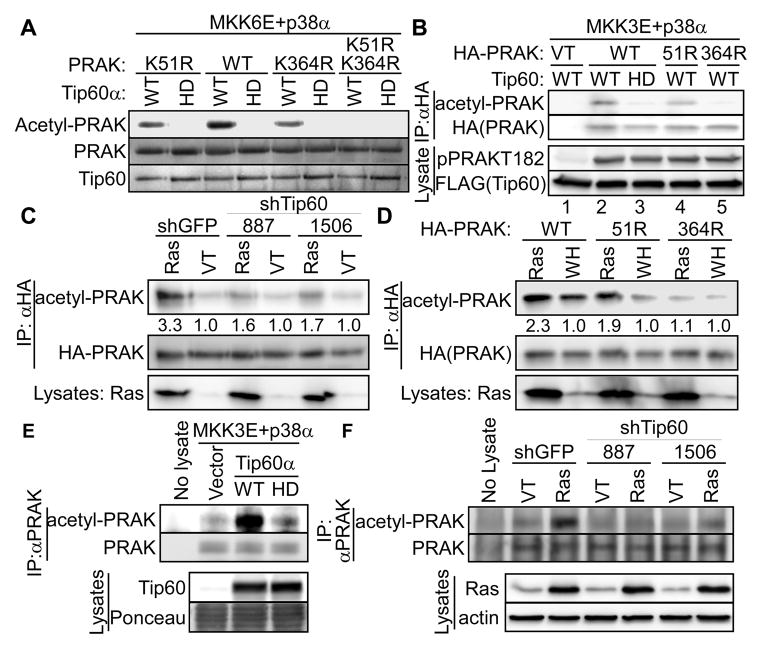
Fig. 6.
Tip60 acetylates PRAK at K364 in vitro and during oncogenic ras-induced senescence.
(A) Wild type (WT) or indicated mutant of recombinant PRAK was incubated with wild type (WT) or HAT-defective (HD) Tip60α and acetyl-CoA in the presence of p38α and MKK6E. Acetylation of PRAK was detected by Western blotting using an anti-acetyl-Lys antibody. Recombinant proteins were stained by Ponceau.
(B) HA-PRAK was immunoprecipitated from 293T cells transfected with wild type (WT) or indicated mutant of HA-PRAK or vector (VT) and wild type (WT) or HAT-defective (HD) Tip60α.
(C) HA-PRAK was immunoprecipitated from BJ cells transduced with HA-PRAK, shRNA for GFP or Tip60 (887, 1506), and HaRasV12 or vector (VT).
(D) HA-PRAK was immunoprecipitated from BJ cells transduced with wild type (WT) or indicated mutant of HA-PRAK, and HaRasV12 or vector (WH).
(E) Endogenous PRAK was immunoprecipitated from 293T cells transfected with wild type (WT) or HAT-defective (HD) Tip60α or vector, MKK3E and p38α.
(F) Endogenous PRAK was immunoprecipitated from BJ cells transduced with shRNA for GFP (shGFP) or Tip60 (887 or 1506) and HaRasV12 (Ras) or vector (VT).
(B–F) Acetylated PRAK and total immunoprecipitated PRAK were detected by Western blotting using an anti-acetyl-Lys antibody and an anti-HA (B–D) or anti-PRAK (E–F) antibody, respectively. Part of the lysates was also analyzed by Western blotting.
(C–D). Numbers are fold induction of acetyl-PRAK signals by ras, after normalizing to the levels of total HA-PRAK.
See also Figure S5.