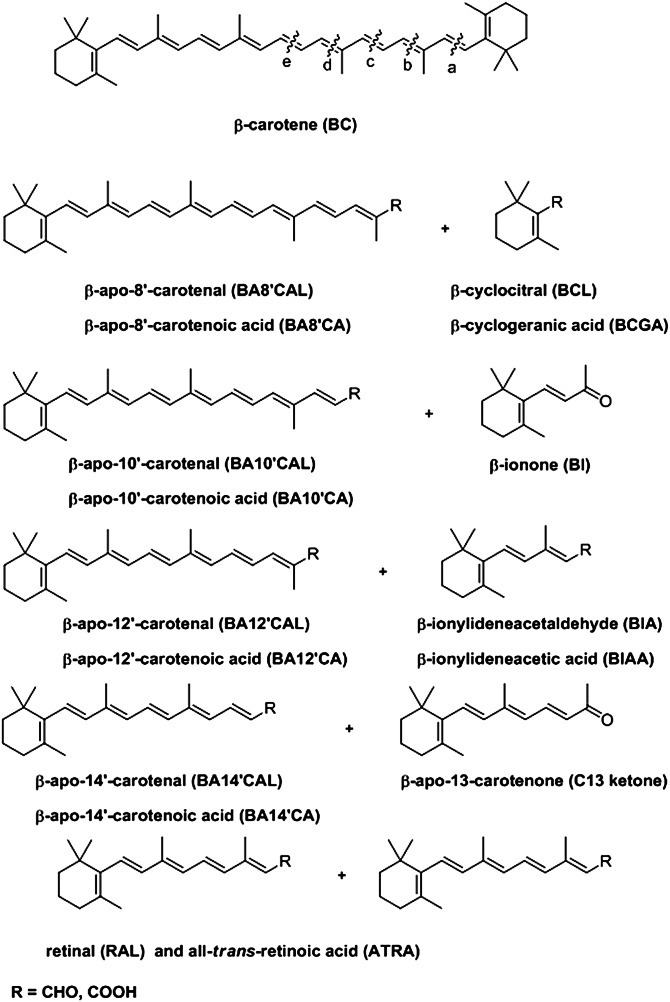
Fig. 1.
Structures and nomenclature of the β-apocarotenoids. All possible β-apocarotenoids arising from oxidative cleavage of β-carotene. Initial products are β-apocarotenals (aldehydes, R = CHO) and, in some cases, β-apocarotenones (ketones). (Top) Cleavages are shown between carbon atoms at the following positions in the β-carotene molecule: (a) 7′, 8′ (b) 9′, 10′ (c) 11′, 12′ (d) 13′, 14′ and (e) 15, 15′. It is possible that in cells the aldehydes can be reduced to the corresponding alcohols by aldehyde reductases and/or alcohol dehydrogenases and can be oxidized to the corresponding carboxylic acids (R = COOH) by aldehyde dehydrogenases.