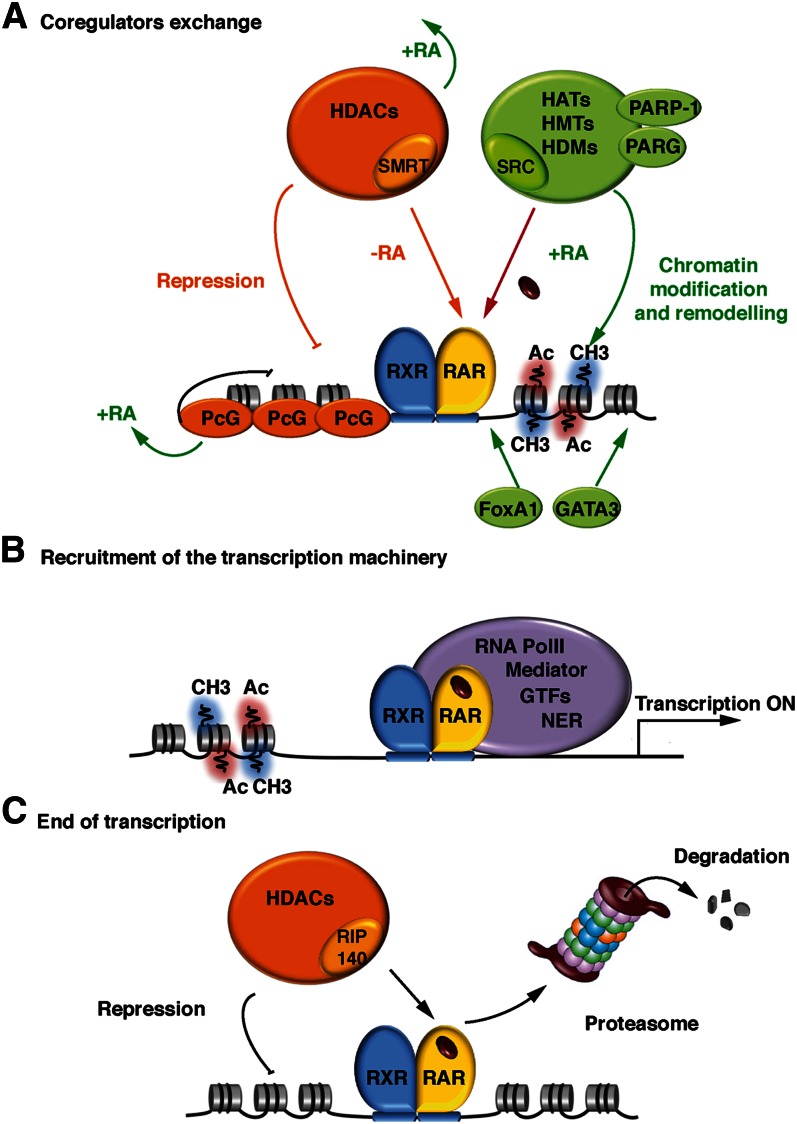
Fig. 4.
Coregulator exchange at RXR/RAR heterodimers. (A) In the absence of ligand, RARα/RXR heterodimers bound to DNA are associated with corepressor complexes. Upon ligand binding, the corepressors dissociate, allowing the recruitment of coactivators and large complexes with enzymatic activities that decompact repressive chromatin. (B) When chromatin is decompacted, the transcriptional machinery, consisting of the Mediator, RNA PolII, the general transcription factors (GTF), and the nuclear excision repair (NER) factors, is recruited to the promoter, resulting in the initiation of transcription. (C) Transcription ends with the recruitment of nonconventional coactivators, such as RIP140, associated to large complexes with chromatin-repressing activity and/or through the degradation of RARs by the ubiquitin-proteasome system.