Figure 3.
The Ctf19 Complex Recruits DDK to Centromeres and Facilitates Early Replication of Centromeric Regions
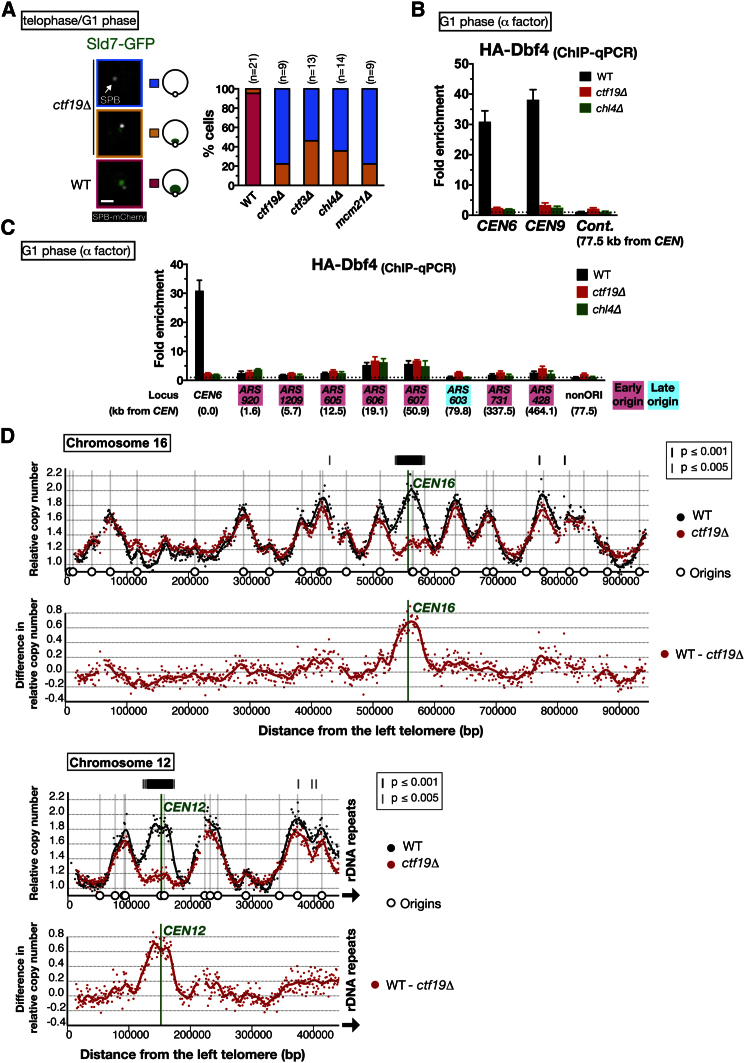
(A) Sld7 localization on centromeric regions is abolished in mutants of the Ctf19-complex components. WT (T8613), ctf19Δ (T9650), ctf3Δ (T9708), chl4Δ (T9709), and mcm21Δ (T9710) cells with SLD7-GFP SPC42-mCherry were observed in asynchronous culture. Cells in telophase–G1 phase were selected. The scale bar represents 1 μm.
(B) Dbf4 association with centromeres is reduced in ctf19Δ and chl4Δ cells. WT (T9945), ctf19Δ (T10275), and chl4Δ (T10278) cells with HA-DBF4 were treated with α factor for 2.5 hr and processed for ChIP using a hemagglutinin (HA) antibody. Coprecipitated DNA was analyzed with qPCR at CEN6, CEN9, and a control locus (PHO4, 77.5 kb from CEN6). The ratio of immunoprecipitated DNA to total DNA in whole-cell extract is normalized relative to a control locus in WT (fold enrichment). Error bars represent SD.
(C) Dbf4 association with replication origins in G1 phase. ChIP-qPCR was performed as in (B) and analyzed at replication origins and the nonorigin (nonORI) locus (PHO4). Error bars represent SD.
(D) Replication of centromeric regions is specifically delayed in ctf19Δ cells. S phase and G2–M phase cells were collected from a culture of WT (T9475) and ctf19Δ (T10117) homozygous diploids. The ratio of the copy number in S phase cells to that in G2–M phase cells is normalized and shown between 1.0 and 2.0 at each chromosome locus. The difference in the replication timing between the two strains is shown at bottom. Smoothed lines were added in both graphs.
See also Figures S2 and S3.