Figure 3.
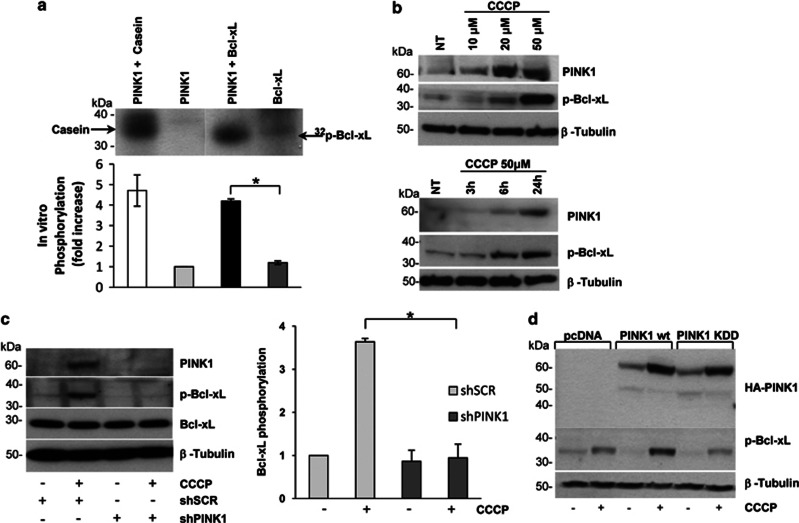
PINK1 phosphorylates Bcl-xL. (a) Mix beads in vitro kinase assay. Immunopurified PINK1 and Bcl-xL were processed as described in the Methods section. Casein was used as a positive control of the PINK1 kinase activity. PINK1 and Bcl-xL alone were used as negative controls. Bcl-xL phosphorylation significantly increased in the presence of PINK1 (4.12±0.10, P=0.001). (b) In vivo phosphorylation of endogenous Bcl-xL. SH-SY5Y cells were either subjected to increasing concentration of CCCP (upper panel) or treated with 50 μM CCCP up to 24 h (lower panel). Lysates were processed for western blotting using p-Bcl-xL and PINK1 antibodies. (c) Bcl-xL phosphorylation upon PINK1 silencing. Lysates from SH-SY5Y cells infected with either shSCR or shPINK1 were treated with 50 μM CCCP for 24 h. PINK1 silencing and p-Bcl-xL levels were assessed by immunoblotting. Densitometric analysis revealed a significant reduction of p-Bcl-xL in CCCP-treated shPINK1 cells compared with control (0.95±0.31 versus 3.63±0.08, P=0.007). (d) Bcl-xL phosphorylation after overexpression of PINK1. Lysates from CCCP-treated SH-SY5Y cells transfected with vector alone (pcDNA), PINK1 wt or KDD were processed for western blotting using HA and p-Bcl-xL antibodies. *P-values<0.05