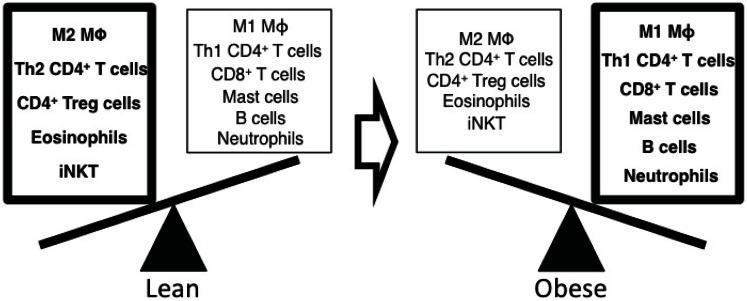
Figure 2.
Altered composition of immune cells with obesity regulates the inflammatory responses in adipose tissue. Alternatively activated M2 macrophages, Th2 CD4+ T cells, regulatory CD4+ T cells (Treg), eosinophils, and iNKT cells are dominant immune cells in adipose tissue of lean mice. These cells secrete anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-4 and IL-10 to suppress inflammation and maintain insulin sensitivity in adipose tissue. In obese mice, the composition of immune cells is dynamically shifted to enhance inflammatory responses in adipose tissue. Classically activated M1 macrophages, Th1 CD4+ T cells, effector CD8+ T cells, mast cells, B cells, and neutrophils are increased and produce inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α, IFN-γ, autoantibodies, and elastase resulting in insulin resistance.