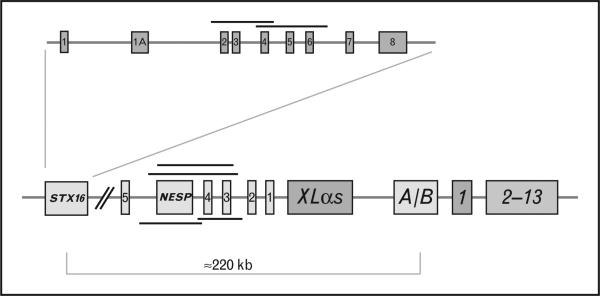
FIGURE 1.
GNAS gene. General organization of the GNAS gene complex and the STX16 gene. The GNAS gene complex consists of 13 exons that encode the signaling protein Gαs. Upstream of exon 1 are three alternative first exons that are labeled exon A/B, XLαs, and Nesp55; exons 1–5 for the NESP antisense transcript are also depicted. The three alternative exons are spliced to exons 2–13 to produce unique transcripts (see text). Nesp55 is transcribed exclusively from the maternal allele; XLαs, AS, and exon A/B are transcribed exclusively from the paternal allele. Nesp AS (antisense) and exon A/B transcripts produce noncoding RNAs. Gαs transcripts are biallelically expressed except in a small number of tissues, such as the renal proximal tubules, thyroid, gonads and pituitary somatotrophs, in which expression is preferentially from the maternal allele. The nine coding exons of the STX16 gene are shown above the GNAS locus, and the locations of deletions in STX16, NESP55 and antisense are shown as black lines (see text).