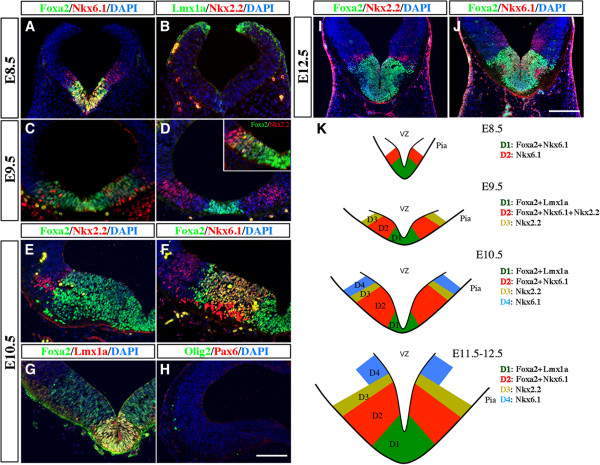
Figure 1.
Distinct progenitor domains in the developing ventral midbrain (vMB) defined by a combinatorial code of transcription factors. (A-D) Double immunostaining for (A,C) Foxa2/Nkx6.1, (B,D) Lmx1a/Nkx2.2 and (inset) Foxa2/Nkx2.2 in vMB at embryonic day (E)8.5 (nine somites) and E9.5. (A) At E8.5, Foxa2 and Foxa2/Nkx6.1 defines domain D1 and D2. (B) Note that Lmx1a and Nkx2.2 are not expressed at E8.5. (C,D) At E9.5, Lmx1a/Foxa2, Foxa2/Nkx6.1, and Nkx2.2 define domains D1 to D3, respectively. (E-J) Confocal images show the expression pattern of (E,I) Foxa2/Nkx2.2, (F,J) Foxa2/Nkx6.1, (G) Foxa2/Lmx1a and (H) Olig2/Pax6 in vMB at E10.5 and E12.5. At both stages, Lmx1a/Foxa2, Foxa2/Nkx6.1, Nkx2.2-only and Nkx6.1-only define domains D1 to D4, respectively. Unlike in the ventral spinal cord, Olig2 and Pax6 were not detected in vMB at E10.5 Scale bars: (H) 50 μm, applied to A-H; (J) 100 μm, applied to I-J. (K) Schematic diagrams illustrating the D1 to D4 progenitor domains in vMB defined by a combinatorial code of transcription factors from E8.5 to E12.5.