Figure 6.
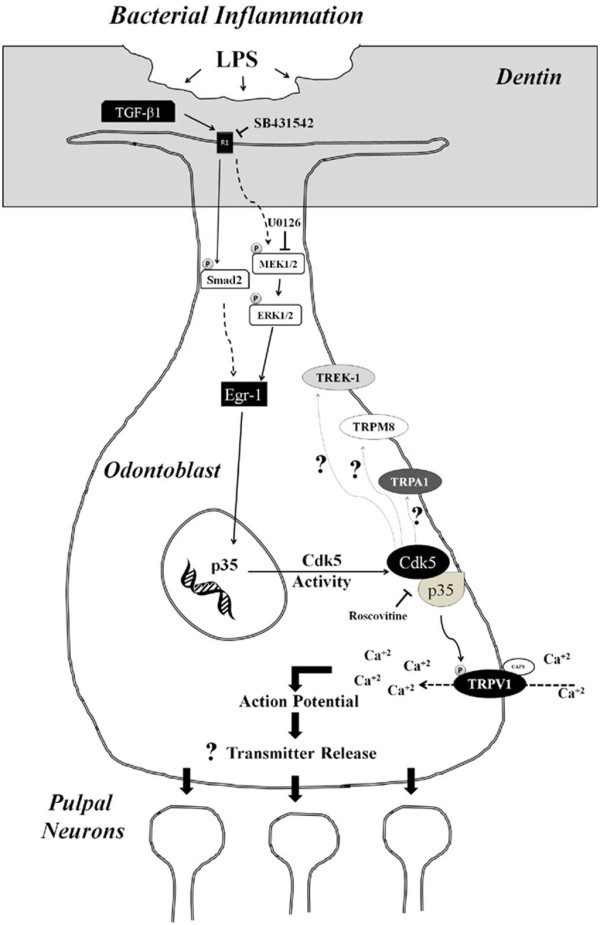
Proposed model illustrating the participation of Cdk5 in signaling pathways that influence dental nociception. Bacterial inflammation occurring in dental caries increases secretion of TGF-β1 into the extracellular matrix, which in turn activates Smad dependent and independent pathways in odontoblast cells. These cascades activate Cdk5 activity by increasing Egr-1 and p35 expression. Then, the Cdk5/p35 complex phosphorylates TRPV1, resulting in enhanced calcium influx and the subsequent activation of action potentials, which in turn may increase transmitter release. Pain transmission would occur through transmitter-mediated activation of pulpal neurons. Moreover, Cdk5 may modulate the sensitivity of other nociceptors such as TRPA1, TRPM8, or TREK-1 during inflammation-induced tooth pain.
