Fig. 5.
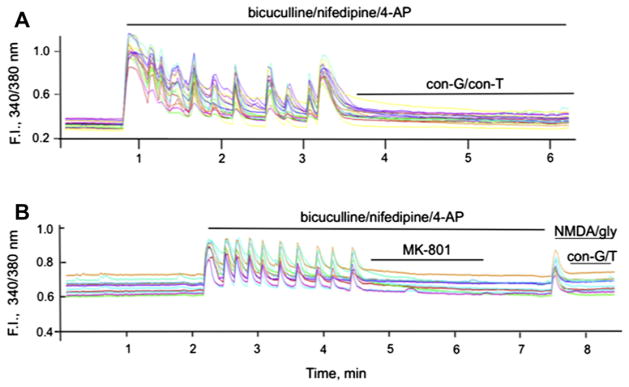
Conantokins inhibit iCa2+ uptake via synaptic or extrasynaptic NMDARs in rat hippocampal neurons. A. Single cell Ca2+ transients measured as 340/380 fluorescence intensity (F.I.) ratio in DIV 13–15 rat hippocampal neurons triggered by activation (50 μM bicuculline/5 μM nifepidine/2.5 mM 4-AP) of the synaptic NMDARs, followed by application of 40 μM con-G or 40 μM con-T. The pulses of synaptic activity were blocked by both conantokins. B. Measure of iCa2+ influx via extrasynaptic NMDARs. Synaptic NMDARs stimulated by 50 μM bicuculline/5 μM nifepidine/2.5 mM 4-AP were first irreversibly blocked by 10 μM MK-801. After a wash period, extrasynaptic NMDARs were activated by bath application of 50 μM NMDA/10 μM glycine, leading to a spike in iCa2+ influx from extrasynaptic NMDARs that was effectively inhibited by the presence of 40 μM con-G or 40 μM con-T. In each case, individual data are shown for 9–10 separate neurons at DIV 13–15.
