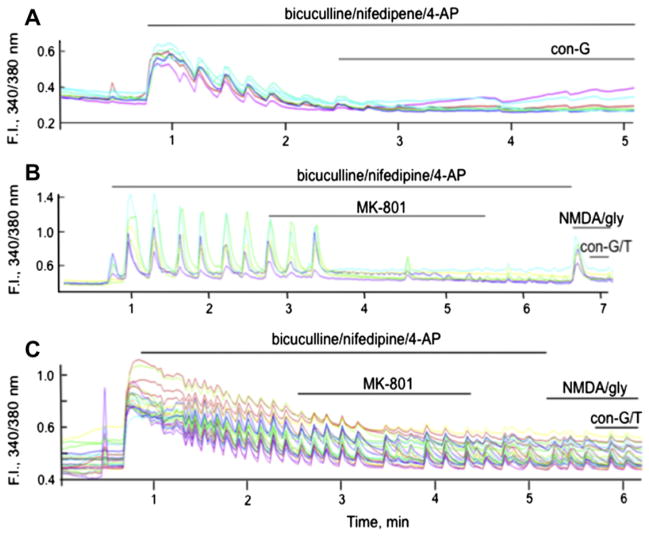
Fig. 6.
Effect of the NMDAR subunit composition on inhibition of synaptic and extrasynaptic iCa2+ uptake in mouse cortical neurons. A. Uptake of Ca2+ by synaptic NMDARs is inhibited by 40 μM con-G in NMDARs of NR2A−/− neurons. B. After blocking synaptic NMDARs by MK-801, extrasynaptic NMDARs were activated by 50 μM NMDA/10 μM glycine, resulting in a spike of iCa2+ resulting from extrasynaptic transport in NR2A−/− neurons. Both 40 μM con-G and 40 μM con-T inhibited this process. C. In a similar experiment with NR2B−/− neurons, 10 μM MK-801 was a poor inhibitor of synaptic currents and NMDA/gly did not activate extrasynaptic NMDAR ion channels. In each case, individual data are shown for 9–10 separate neurons at DIV 13–15.