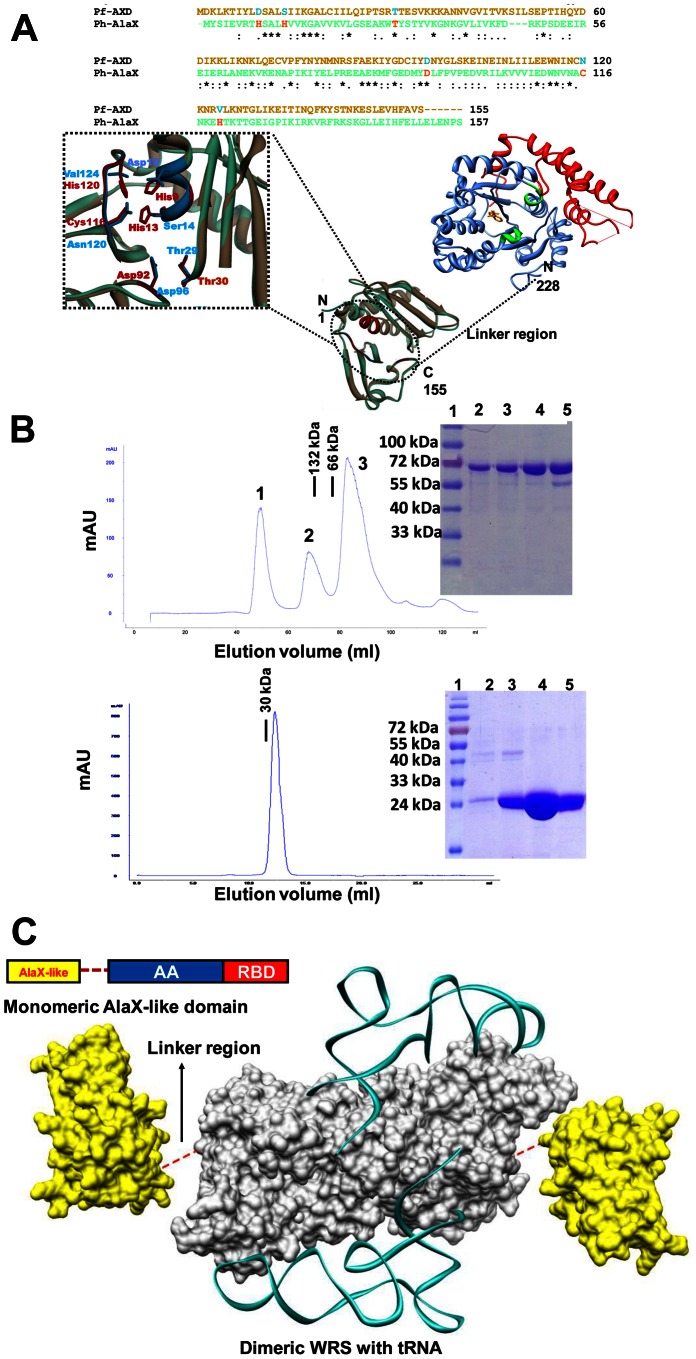
Figure 3. Domain architecture, structural modeling and gel permeation chromatography of Pf-WRS.
(A). Sequence alignment of AlaX-like domain present in N-terminal region of Pf-WRS with AlaX (top). The critical active site residues of AlaX are shown but are not conserved in AXD. Three-dimensional model for Pf-WRS AXD is shown attached via a linker to main protein body (B). Size exclusion chromatography profile for full length Pf-WRS (residue 1–632, dimeric molecular weight ∼140 kDa) is shown on top panel. Protein purification was monitored by using UV (280 nm) absorbance in all experiments. The three major protein peaks in correspond to 1) insoluble protein aggregates, 2) Pf-WRS (which migrates as a dimer) and 3) cleaved MBP-fusion tag (migrates as a monomer of 42K) respectively. The bottom panel displays migration of NTD at expected molecular weight and as a monomer. In both cases, SDS-PAGE shows full length Pf-WRS (4 lanes, single bands of ∼73 kDa) in upper panel, and NTD (single band of ∼26 kDa) in lower panel. These fractions were recovered as peaks in the gel filtration runs. The molecular weight markers are BSA (132 kDa and 66 kDa) and DTD (30K) shown by black bars. Gel filtration chromatography was performed for NTD on Superdex75 column (void volume - 7 ml) and for FLP on Superdex200 column (void volume - 40 ml) respectively (C). Modeling of the overall architecture of full length Pf-WRS where monomeric NTDs (yellow) are attached to both to the dimeric catalytic cores (grey). Wire diagram shows modeled tRNA based on crystal structure of human-WRS in complex with tRNA.