Figure 6. Sequence, structure, electrostatic and motif comparisons between Pf-WRS and Hs-WRS.
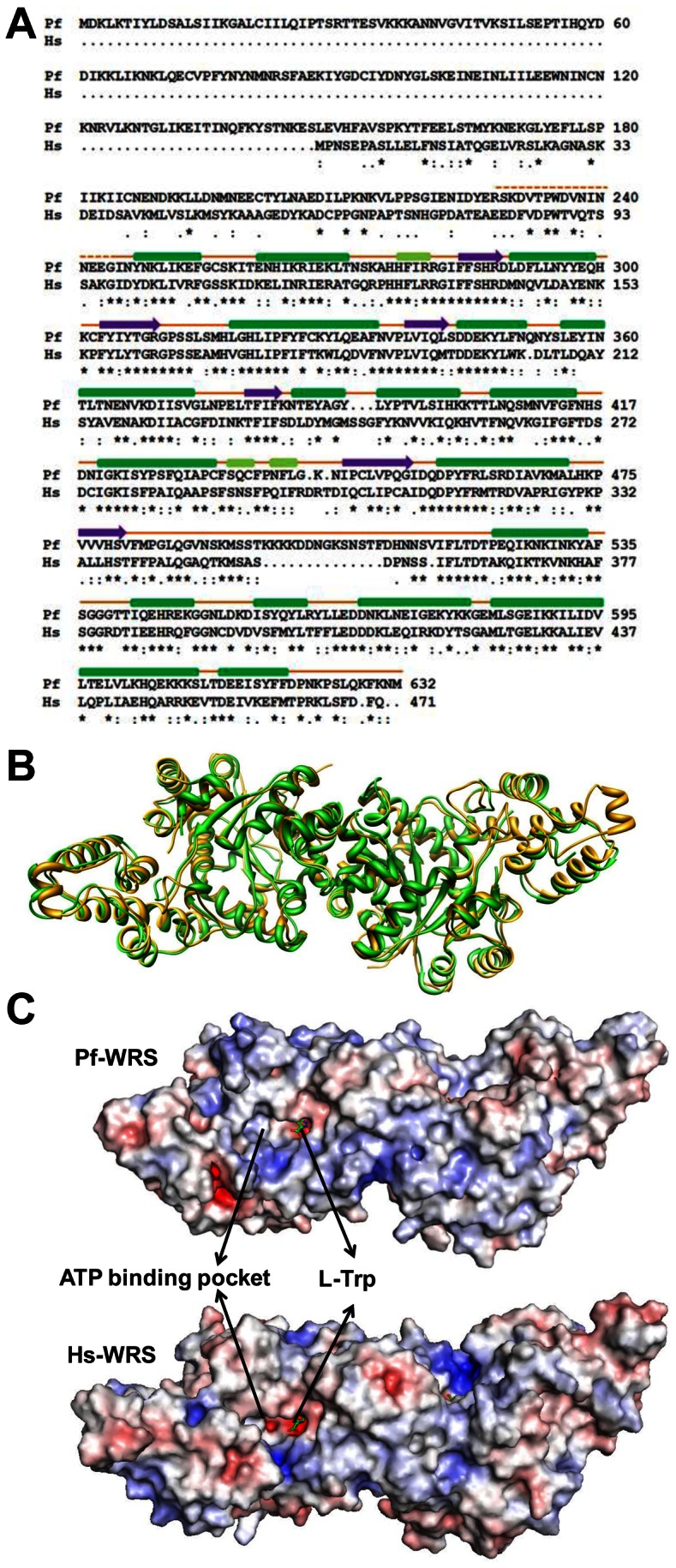
(A). Highly conserved residues, conserved ones, and semi-conserved residues are marked with asterisks, semicolons and dots respectively. The three conserved motifs HLGH, GIDQ and KMSST are shown in red boxes. L-Trp (red), K+ ion (blue) interacting residues and insertion residues (purple) in KMSST loop are highlighted (B). Superposition of Pf-WRS dimers (green) with Hs-WRS (gold) shows the high degree of structural conservation in the catalytic domains of each (C). Comparison of electrostatic surfaces of Pf-WRS and Hs-WRS. The electrostatic surfaces are displayed as color gradients in red (electronegative, ≤−10 kTe−1) and blue (electropositive, ≥10 kTe−1) (D). Left panel shows superposition of two human-WRS structures in red (105T) and green (1ULH). In both cases, the ATP binding pocket is devoid of ligand and the KMSAS loop (in blue) is ordered. Right panel shows superposition of two human-WRS structures in red (105T) and green (2QUI) where the former is in apo form whereas the latter has ATP (in yellow) bound. Once again, the KMSAS loop (in blue) is ordered in both cases.
