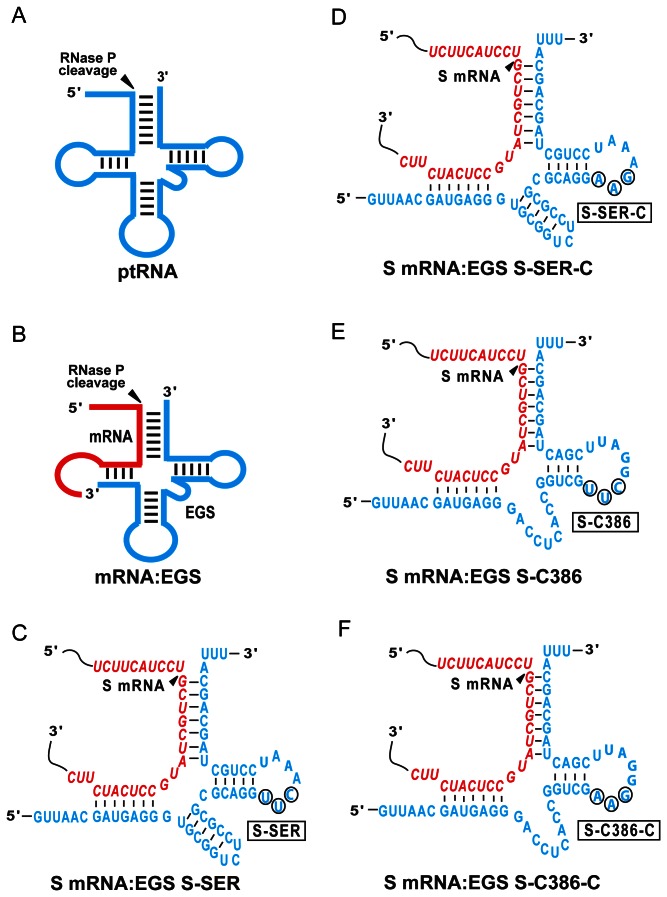
Figure 1. Substrates for RNase P.
(A) A natural substrate (ptRNA). (B) A hybridized complex of a target RNA (e.g. mRNA) and an EGS resembling the structure of a tRNA. (C, D, E, and F) Complexes between HBV S mRNA (S RNA) sequence and EGS S-SER, S-SER-C, S-C386, and S-C386-C, respectively. The sequences of S-SER and S-SER-C that were equivalent to the T-stem and loop, and variable region of a tRNA molecule were derived from tRNASer, while those of S-C386 and S-C386-C were from EGS variant C386. Only the exact sequence of the S mRNA around the targeting site is shown (in red) and the EGS sequence is shown in blue color. The site of cleavage by RNase P is marked with an arrowhead.