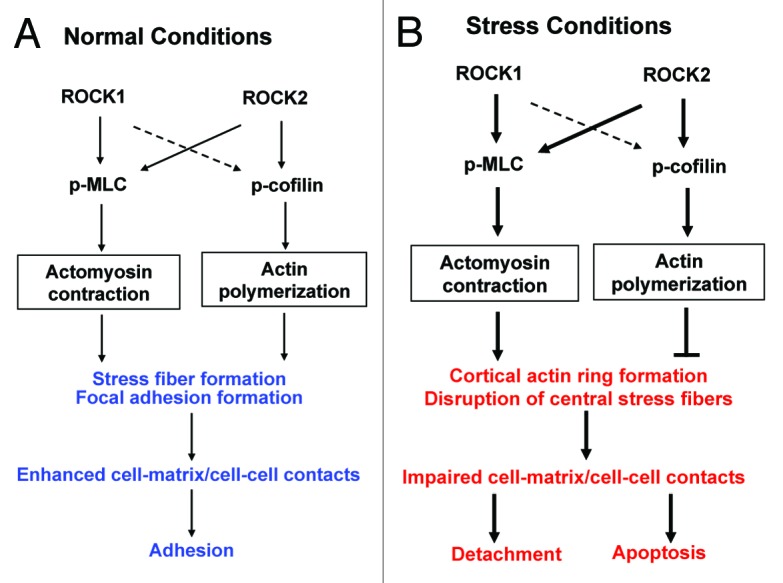
Figure 8. Schematic summary of roles of ROCK1 and ROCK2 in regulating actin cytoskeleton organization under normal (A) or cytotoxic stress (B) conditions (e.g., doxorubicin or serum starvation). Both ROCK1 and ROCK2 are involved in promoting actomyosin contraction via MLC phosphorylation. ROCK2 plays a preferential role in promoting actin polymerization via cofilin phosphorylation. Under normal conditions, both actomyosin contraction and actin polymerization promote stress fiber formation and focal adhesion formation resulting in cell adhesion. Under stress conditions, increased actomyosin contraction and actin polymerization play opposite roles in cortical ring formation and central stress fiber disruption. These stress-induced actin cytoskeleton remodeling events lead to cell detachment and apoptosis. The thin solid lines stand for baseline action. The thick solid lines stand for stimulated actions. The broken lines stand for alternative actions in the absence of ROCK2.
