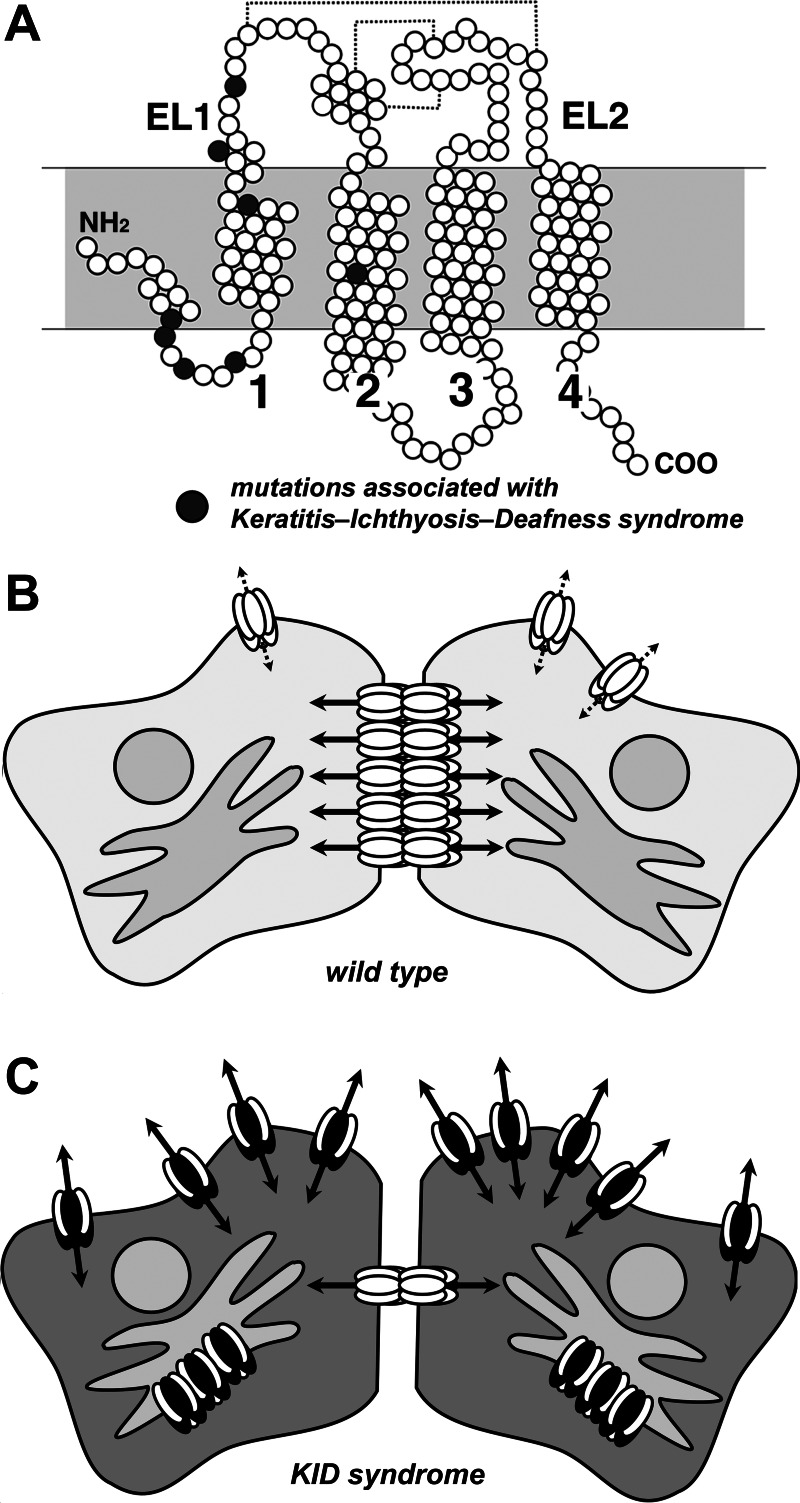
Fig. 1.
Effects of mutant connexin 26 (Cx26) on gap junction hemichannels. A: structure of Cx26. Shown is a diagram depicting individual amino acids of Cx26 as circles. Filled circles represent amino acid positions mutated in keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness (KID) syndrome. Indicated are the first and second extracellular loop domains (EL1 and EL2) as well as the four transmembrane domains. Dashed lines represent disulfide bonds between EL1 and EL2. B: cells expressing wild-type Cx26 (white ovals) primarily form gap junction channels (solid arrows) and have minimal hemichannel activity (dashed arrows). Here only Cx26 is shown for simplicity; cells in the cochlea or skin express other connexins in addition to Cx26. C: cells expressing mutant Cx26 (dark ovals) interact with wild-type Cx26 to inhibit trafficking and formation of gap junction channels. Instead Cx26 hemichannels show increased activity that impairs cell function.