Fig. 1.
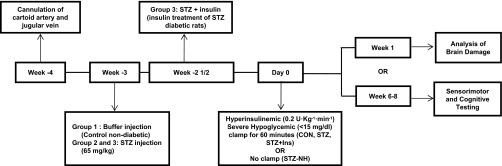
Experimental protocol. After recovery from arterial and venous cannulation, rats were injected with streptozotocin (STZ) or vehicle (CON; n = 18). Three days later, insulin treatment was started in a subset of the STZ-diabetic rats (STZ + Ins; n = 15) by implanting an insulin pellet and starting insulin injections as needed to maintain blood glucose <250 mg/dl. About 3 wk later, hyperinsulinemic (0.2 U·kg−1·min−1) severe hypoglycemic (10–15 mg/dl) clamps were performed in all rats, except for a group of diabetic rats that were not subjected to the severe hypoglycemic clamp (STZ-NH). After the episode of severe hypoglycemia, either neuronal damage was assessed by Flouro-Jade B and hematoxylin-eosin staining 1 wk later or rats were studied 6–8 wk later with sensorimotor and cognitive testing. Brain damage study: CON (n = 6), STZ (n = 6), and STZ + Ins (n = 6); cognitive testing study: CON (n = 12), STZ (n = 13), STZ + Ins (n = 12), and STZ-NH (n = 10).
