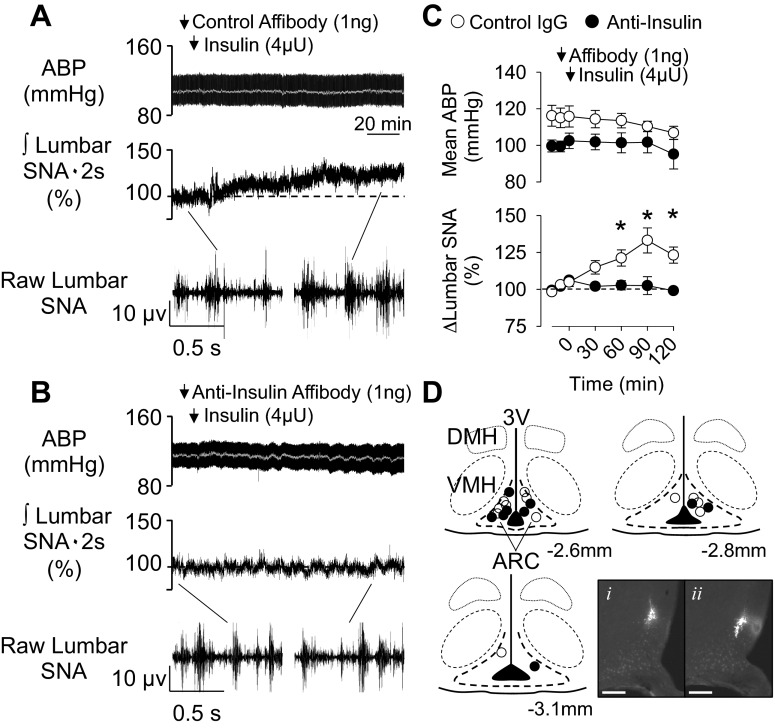
Fig. 1.
Anti-insulin affibody prevents the sympathoexcitatory response to insulin in the arcuate nucleus (ARC). A and B: arterial blood pressure (ABP) and mean ABP (gray line) (top), integrated (∫) lumbar sympathetic nerve activity (SNA; middle), and raw lumbar SNA (bottom; 1-s segments) of rats that received an injection of the control antibody (A; n = 6) or anti-insulin affibody (B; n = 4) into the ARC 10 min before ARC injection of insulin. C: mean ± SE values of mean ABP and lumbar SNA. *P < 0.05, control vs. anti-insulin affibody. Arrows denote ARC injection. D: schematic illustration and photomicrographs of ARC injection sites. Coordinates are rostrocaudal levels in reference to the bregma using the atlas of Paxinos and Watson. (36). The photomicrograph shows the injection site for red (i) and green (ii) beads for the same animal, although sections are 80 μm apart. Scale bars = 200 μm. DMH, dorsomedial hypothalamus; VMH, ventromedial hypothalamus; 3V, third ventricle.